MicroRNA expression levels as diagnostic biomarkers for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
- PMID: 28938594
- PMCID: PMC5601690
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17679
MicroRNA expression levels as diagnostic biomarkers for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
Abstract
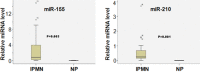
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) are deadly exocrine mucinous tumors. Currently the molecular features and diagnostic markers of IPMNs are not well understood. In this study, we performed microRNA (miRNA) profiling assays to study the potential roles of miRNAs in IPMNs using 78 cases of IPMN patients and controls. When comparing the miRNA expression between IPMN patient samples and controls, we found that miR-210, miR-223, miR-221, miR-155 and miR-187 were differentially expressed in normal pancreas and IPMNs. We further studied the miRNA expression profiles in different pancreatic diseases and identified miRNA features that are associated with Chronic pancreatitis (CP), IPMN, and Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Therefore, these miRNAs might serve as new risk biomarkers of IPMN and could be useful for future targeted therapies.
Keywords: cancer diagnosis; intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs); miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA as screening biomarkers for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.Oncol Lett. 2020 Dec;20(6):315. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12178. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33133251 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide investigation of microRNA expression identifies biologically-meaningful microRNAs that distinguish between high-risk and low-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 21;10(1):e0116869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116869. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25607660 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for Patients with Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2015 Sep;8(9):826-34. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0094. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2015. PMID: 26314797 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016 Jan 15;8(1):18-29. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i1.18. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26798434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas: Current Perspectives.Int Surg. 2015 Jun;100(6):1060-8. doi: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-14-00220.1. Int Surg. 2015. PMID: 26414828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PDS5A and PDS5B in Cohesin Function and Human Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 30;22(11):5868. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115868. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of EUS-based techniques in the evaluation of pancreatic cystic neoplasms.Endosc Ultrasound. 2021 Jul-Aug;10(4):230-240. doi: 10.4103/EUS-D-20-00216. Endosc Ultrasound. 2021. PMID: 34213426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevating pancreatic cystic lesion stratification: Current and future pancreatic cancer biomarker(s).Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020 Jan;1873(1):188318. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188318. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31676330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-223-3p in Cancer Development and Cancer Drug Resistance: Same Coin, Different Faces.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8191. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158191. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Host miRNAs Correlated with Immune Gene Dysregulation during Fatal Disease Progression in the Ebola Virus Cynomolgus Macaque Disease Model.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 23;9(3):665. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030665. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33806942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nara S, Onaya H, Hiraoka N, Shimada K, Sano T, Sakamoto Y, Esaki M, Kosuge T. Preoperative evaluation of invasive and noninvasive intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical, radiological, and pathological analysis of 123 cases. Pancreas. 2009;38:8–16. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318181b90d. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

