Multiple receptor tyrosine kinase activation related to ALK inhibitor resistance in lung cancer cells with ALK rearrangement
- PMID: 28938595
- PMCID: PMC5601691
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17680
Multiple receptor tyrosine kinase activation related to ALK inhibitor resistance in lung cancer cells with ALK rearrangement
Abstract
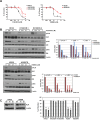
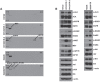
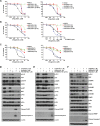
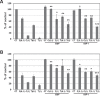
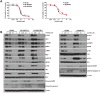
The activation of alternative receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) is known to mediate resistance to ALK inhibitors. However, the role of multiple RTK activation in resistance has yet to be determined. Two crizotinib-resistant (H3122/CR-1 and H3122/CR-2) and one TAE684-resistant (H2228/TR) cell lines were established. Multi-RTK arrays and Western blots were performed to detect the activation of bypass signals. There were no secondary mutations in the sequencing. EGFR and MET were activated in H3122/CR-1 cells whereas EGFR and IGF1R were activated in H3122/CR-2 cells. Concomitant activation of MET did not contribute to resistance as crizotinib completely suppressed both p-MET and p-ALK in H3122/CR-1 cells, whose survival was not affected by crizotinib. However, combined inhibition of EGFR and ALK was effective in controlling this resistant cell line. In H3122/CR-2 cells, the inhibition of both ALK and IGF1R could effectively suppress cell growth, whereas simultaneous inhibition of ALK and EGFR brought about a less-effective suppression, indicating that IGF1R activation is the main resistance mechanism. H2228/TR cells showed activation of the HER family (EGFR, ErbB2, and ErbB3). Afatinib, a pan-HER inhibitor, was more potent in suppressing resistant cells than gefitinib when combined with crizotinib, which suggests that coactivation of ErbB2 and ErbB3 also contributes to resistance. Interestingly, all three resistant cell lines responded well to AUY922, which can inhibit ALK, EGFR, and IGF1R activity. Activation of multiple RTKs can occur during acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors, in which case the dominant or significant bypass signal should be identified to provide a more appropriate combination therapy.
Keywords: ALK; EGFR; IGF1R; lung cancer; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K, Hatanaka H, Bando M, Ohno S, Ishikawa Y, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crino L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, Wu YL, Thomas M, O'Byrne KJ, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2385–2394. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

