Dickkopf-1 induces angiogenesis via VEGF receptor 2 regulation independent of the Wnt signaling pathway
- PMID: 28938611
- PMCID: PMC5601707
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19769
Dickkopf-1 induces angiogenesis via VEGF receptor 2 regulation independent of the Wnt signaling pathway
Abstract
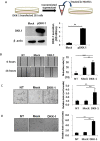
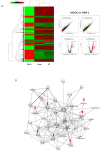
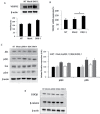
Tumor angiogenesis is essential for invasive tumor growth and metastasis. Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1), an antagonist of Wnt signaling, participates in tumor development and progression. We evaluated whether DKK-1 stimulation induces angiogenesis and the endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EnMT). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were stimulated with recombinant DKK-1 (rDDK-1) or conditioned medium from a culture of DKK-1-transfected 293 cells. Following stimulation, the expression levels of angiogenesis-related factors and EnMT related markers were determined by immunoblot assays. In addition, the effects of exogenous DKK-1 on angiogenesis and EnMT were assessed by tube-formation, cell invasion, and wound-healing assays. Human hepatoma cells, such as Hep3B and Huh-7, showed high levels of DKK-1 expression, whereas 293 cells and HUVECs showed little or no DKK-1 expression. Increased endothelial cell tube formation and invasiveness were observed in HUVECs treated with concentrated conditioned medium from DKK-1-overexpressing 293 cells or rDKK-1. DKK-1-stimulated HUVECs also exhibited increased motility in wound-healing assays. Furthermore, the expression levels of angiogenesis-related factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 and vascular endothelial-cadherin, were increased in DKK-1-stimulated HUVECs. The expression of EnMT markers, such as vimentin and Twist, was also increased in DKK-1-stimulated HUVECs. However, no significant change in β-catenin or GSK3β expression was observed. Our in vitro data suggest that DKK-1 can enhance angiogenesis and EnMT by HUVECs independent of the Wnt signaling pathway. Modulation of DKK-1 expression may facilitate development of novel strategies to control tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.
Keywords: HUVEC; Hepatocellular carcinoma; angiogenesis; dickkopf-1; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sulphonated Formononetin Induces Angiogenesis through Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor/cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein/Early Growth Response 3/Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Pharmacology. 2018;101(1-2):76-85. doi: 10.1159/000480662. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Pharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29131133
-
Dickkopf-3 Upregulates VEGF in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells by Activating Activin Receptor-Like Kinase 1 (ALK1) Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 14;8:111. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00111. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28352232 Free PMC article.
-
DICKKOPF-4 is induced by TCF/beta-catenin and upregulated in human colon cancer, promotes tumour cell invasion and angiogenesis and is repressed by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3.Oncogene. 2008 Jul 24;27(32):4467-77. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.88. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18408752
-
Factors affecting the role of canonical Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 in cancer progression.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 15;13:1114822. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1114822. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37007131 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with a focus on the role of Wnts and the dickkopf family of Wnt inhibitors.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2014 Mar 6;1:1-7. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S44537. eCollection 2014. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2014. PMID: 27508171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum biomarkers of neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier leakage in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.BMC Neurol. 2022 Jun 11;22(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02730-1. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35690735 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive borate glass triggers phenotypic changes in adipose stem cells.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020 Mar 23;31(4):35. doi: 10.1007/s10856-020-06366-w. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020. PMID: 32206916
-
Expression and Role of Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) in Tumors: From the Cells to the Patients.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Jan 25;13:659-675. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S275172. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33536782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/frizzled Signaling in Endothelium: A Major Player in Blood-Retinal- and Blood-Brain-Barrier Integrity.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022 May 17;12(4):a041219. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041219. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022. PMID: 35074794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A promising field: regulating imbalance of EndMT in cardiovascular diseases.Cell Cycle. 2021 Aug;20(15):1477-1486. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1951939. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34266366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, Monaghan AP, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature. 1998;391:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M, Mechler BM, Delius H, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Walter C, Glinka A, Niehrs C. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 2002;417:664–667. - PubMed
-
- González-Sancho JM, Aguilera O, García JM, Pendás-Franco N, Peña C, Cal S, García de Herreros A, Bonilla F, Muñoz A. The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of beta-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:1098–1103. - PubMed
-
- Wirths O, Waha A, Weggen S, Schirmacher P, Kühne T, Goodyer CG, Albrecht S, Von Schweinitz D, Pietsch T. Overexpression of human Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of wingless/WNT signaling, in human hepatoblastomas and Wilms’ tumors. Lab Invest. 2003;83:429–434. - PubMed
-
- Tian E, Zhan F, Walker R, Rasmussen E, Ma Y, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD., Jr The role of the Wnt-signaling antagonist DKK1 in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2483–2494. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

