APE1 overexpression is associated with poor survival in patients with solid tumors: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28938675
- PMCID: PMC5601771
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19814
APE1 overexpression is associated with poor survival in patients with solid tumors: a meta-analysis
Abstract
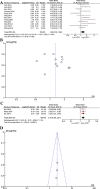
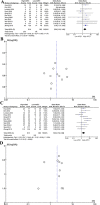
APE1 is known as a key mediator of DNA damage repair pathways, and its clinical significance in different types of cancer is well studied. Herein, we performed a meta-analysis to determine the association of APE1 expression and survival in different types of solid cancer. We searched all eligible publications in PubMed, Web of Science and Embase platforms from inception to January 2017 and found 15 relevant manuscripts. Overall survival (OS), 12- and 36-month survival rates, and hazard ratios (HRs) were extracted and analyzed. Heterogeneity and publication bias were also assessed. A subgroup analysis of the different subcellular locations of APE1 was also conducted. Patients with higher APE1 levels demonstrated lower 12- and 36-month survival rates than those with low APE1 levels (HR 2.00, 95% CI 1.33-3.00, P = 0.0009; HR 1.84, 95% CI 1.19-2.84, P = 0.006). Importantly, the pooled analysis showed that high levels of APE1 predict shorter OS (HR 1.44, 95% CI 1.13-1.83, P = 0.003). Subgroup analysis revealed that both nuclear and cytoplasmic expression levels of APE1 are important indicators of poor prognosis in solid tumors.
Keywords: APE1; IHC; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures


References
-
- Fung H, Demple B. A vital role for Ape1/Ref1 protein in repairing spontaneous DNA damage in human cells. Mol Cell. 2005;17:463–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.12.029. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tell G, Damante G, Caldwell D, Kelley MR. The intracellular localization of APE1/Ref-1: more than a passive phenomenon? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7:367–84. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2005.7.367. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ueno M, Masutani H, Arai RJ, Yamauchi A, Hirota K, Sakai T, Inamoto T, Yamaoka Y, Yodoi J, Nikaido T. Thioredoxin-dependent redox regulation of p53-mediated p21 activation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:35809–15. - PubMed
-
- Yoo DG, Song YJ, Cho EJ, Lee SK, Park JB, Yu JH, Lim SP, Kim JM, Jeon BH. Alteration of APE1/ref-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: the implications of impaired extracellular superoxide dismutase and catalase antioxidant systems. Lung Cancer. 2008;60:277–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.10.015. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

