Clozapine-induced acute gastrointestinal necrosis: a case report
- PMID: 28938913
- PMCID: PMC5610409
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-017-1447-4
Clozapine-induced acute gastrointestinal necrosis: a case report
Abstract
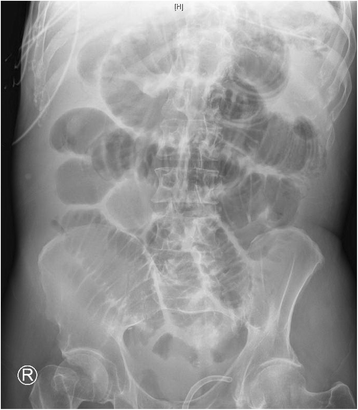
Background: Clozapine is known to cause fecal impaction and ileus with resultant colonic necrosis due to compression of colonic mucosa. There are rare reports of clozapine causing necrosis of other portions of the gastrointestinal tract unrelated to constipation. We describe a case of acute necrosis of the upper gastrointestinal tract and small bowel to due to clozapine and quetiapine.
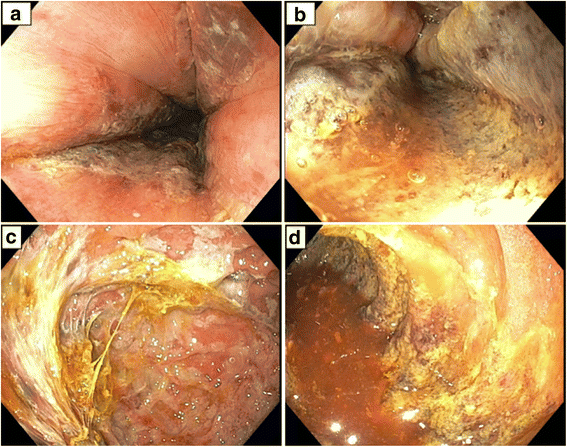
Case presentation: A 66-year-old white man with a past medical history of schizophrenia, maintained on clozapine and quetiapine, presented with hypoxic respiratory failure caused by aspiration of feculent emesis due to impacted stool throughout his colon. His constipation resolved with discontinuation of clozapine and quetiapine, and his clinical condition improved. These medicines were restarted after 2 weeks, resulting in acute gastrointestinal necrosis from the mid esophagus through his entire small bowel. He died due to septic shock with Gram-negative rod bacteremia.
Conclusions: Clozapine may cause acute gastrointestinal necrosis.
Keywords: Acute bowel necrosis; Acute esophageal necrosis; Acute gastrointestinal necrosis; Antipsychotic; Clozapine; Quetiapine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s next of kin for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous