Use of the KlADH3 promoter for the quantitative production of the murine PDE5A isoforms in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis
- PMID: 28938916
- PMCID: PMC5610471
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-017-0779-5
Use of the KlADH3 promoter for the quantitative production of the murine PDE5A isoforms in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis
Abstract
Background: Phosphodiesterases (PDE) are a superfamily of enzymes that hydrolyse cyclic nucleotides (cAMP/cGMP), signal molecules in transduction pathways regulating crucial aspects of cell life. PDEs regulate the intensity and duration of the cyclic nucleotides signal modulating the downstream biological effect. Due to this critical role associated with the extensive distribution and multiplicity of isozymes, the 11 mammalian families (PDE1 to PDE11) constitute key therapeutic targets. PDE5, one of these cGMP-specific hydrolysing families, is the molecular target of several well known drugs used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension. Kluyveromyces lactis, one of the few yeasts capable of utilizing lactose, is an attractive host alternative to Saccharomyces cerevisiae for heterologous protein production. Here we established K. lactis as a powerful host for the quantitative production of the murine PDE5 isoforms.
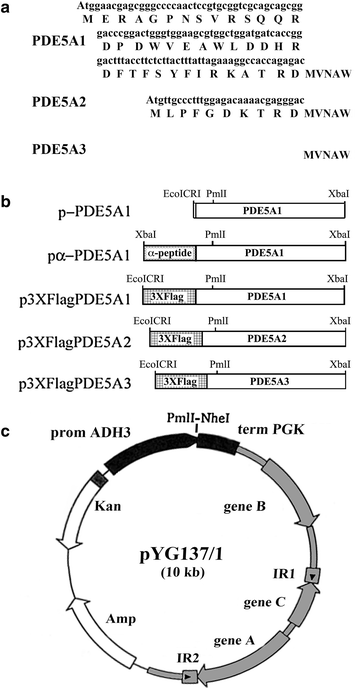
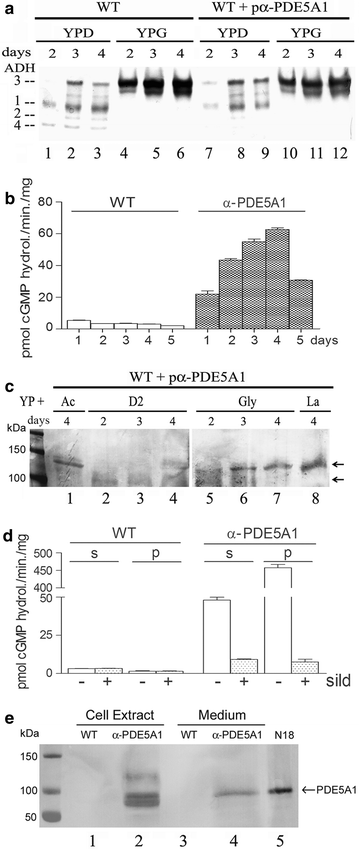
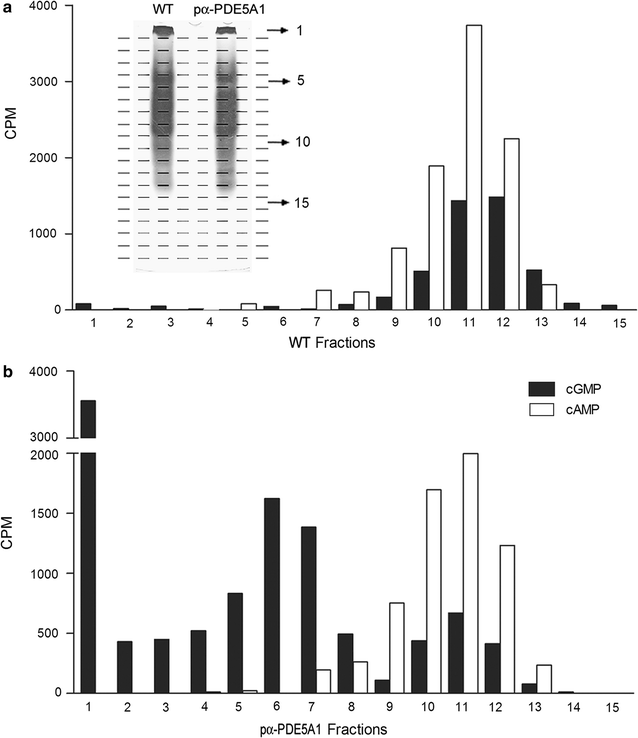
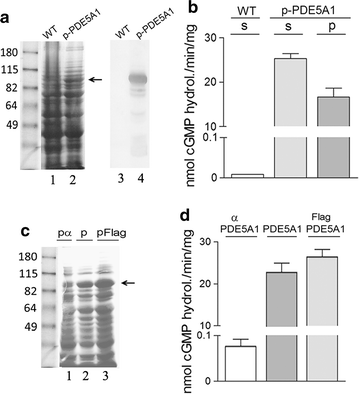
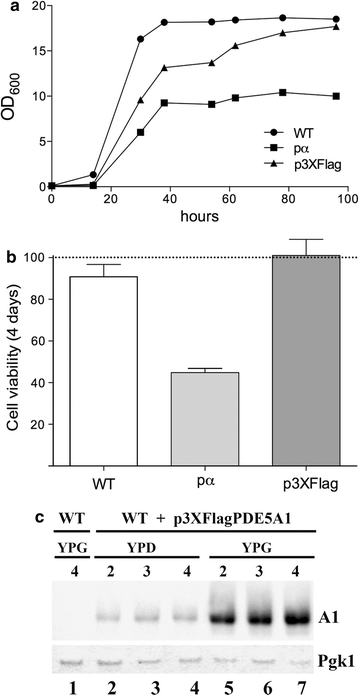
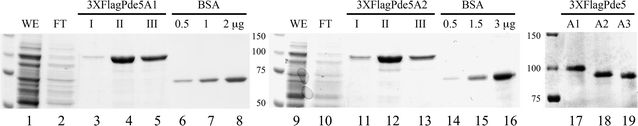
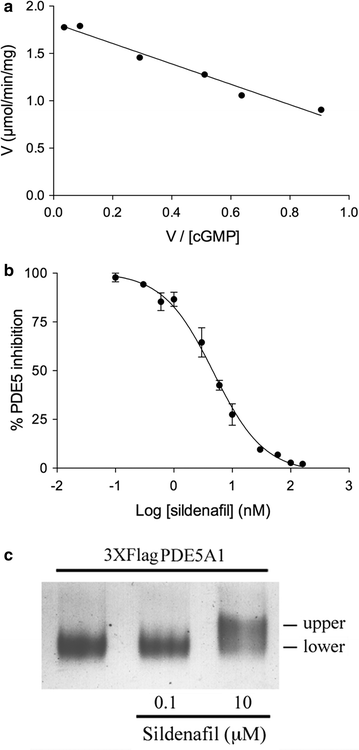
Results: Using the promoter of the highly expressed KlADH3 gene, multicopy plasmids were engineered to produce the native and recombinant Mus musculus PDE5 in K. lactis. Yeast cells produced large amounts of the purified A1, A2 and A3 isoforms displaying Km, Vmax and Sildenafil inhibition values similar to those of the native murine enzymes. PDE5 whose yield was nearly 1 mg/g wet weight biomass for all three isozymes (30 mg/L culture), is well tolerated by K. lactis cells without major growth deficiencies and interferences with the endogenous cAMP/cGMP signal transduction pathways.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first time that the entire PDE5 isozymes family containing both regulatory and catalytic domains has been produced at high levels in a heterologous eukaryotic organism. K. lactis has been shown to be a very promising host platform for large scale production of mammalian PDEs for biochemical and structural studies and for the development of new specific PDE inhibitors for therapeutic applications in many pathologies.
Keywords: KlADH3 promoter; Kluyveromyces lactis; Multicopy plasmids; Murine PDE5; Sildenafil; cGMP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cellular Redox Metabolism Is Modulated by the Distinct Localization of Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase 5A Isoforms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8587. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158587. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955722 Free PMC article.
-
The oligomeric assembly of the phosphodiesterase-5 is a mixture of dimers and tetramers: A putative role in the regulation of function.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Oct;1862(10):2183-2190. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 30025857
-
A Novel Regulated Hybrid Promoter That Permits Autoinduction of Heterologous Protein Expression in Kluyveromyces lactis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jul 1;85(14):e00542-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00542-19. Print 2019 Jul 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31053583 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast Kluyveromyces lactis as an efficient host for heterologous gene expression.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1993-1994;64(2):187-201. doi: 10.1007/BF00873027. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1993. PMID: 8092859 Review.
-
Heterologous protein production in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis.FEMS Yeast Res. 2006 May;6(3):381-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2006.00049.x. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006. PMID: 16630278 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase 5a Signalling in Skeletal Muscle Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 31;24(1):703. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010703. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614143 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Characterization of Murine Phosphodiesterase 5 Isoforms and Involvement of Cysteine Residues in Supramolecular Assembly.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 6;24(2):1108. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021108. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674621 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Redox Metabolism Is Modulated by the Distinct Localization of Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase 5A Isoforms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8587. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158587. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955722 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Monascus yellow pigments production by activating the cAMP signalling pathway in Monascus purpureus HJ11.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Dec 7;19(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01486-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 33287814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keravis T, Lugnier C. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isozymes as targets of the intracellular signalling network: benefits of PDE inhibitors in various diseases and perspectives for future therapeutic development. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165:1288–1305. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01729.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

