Distinct lithium-induced gene expression effects in lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with bipolar disorder
- PMID: 28939162
- PMCID: PMC5685885
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.09.003
Distinct lithium-induced gene expression effects in lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with bipolar disorder
Abstract
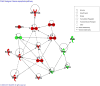
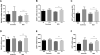
Lithium is the most commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of bipolar disorder (BD), yet the mechanisms underlying its beneficial effects are still unclear. We aimed to compare the effects of lithium treatment in lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from BD patients and controls. LCLs were generated from sixty-two BD patients (based on DSM-IV) and seventeen healthy controls matched for age, sex, and ethnicity. Patients were recruited from outpatient clinics from February 2012 to October 2014. LCLs were treated with 1mM lithium for 7 days followed by microarray gene expression assay and validation by real-time quantitative PCR. Baseline differences between groups, as well as differences between vehicle- and lithium-treated cells within each group were analyzed. The biological significance of differentially expressed genes was examined by pathway enrichment analysis. No significant differences in baseline gene expression (adjusted p-value < 0.05) were detected between groups. Lithium treatment of LCLs from controls did not lead to any significant differences. However, lithium altered the expression of 236 genes in LCLs from patients; those genes were enriched for signaling pathways related to apoptosis. Among those genes, the alterations in the expression of PIK3CG, SERP1 and UPP1 were validated by real-time PCR. A significant correlation was also found between circadian functioning and CEBPG and FGF2 expression levels. In summary, our results suggest that lithium treatment induces expression changes in genes associated with the apoptosis pathway in BD LCLs. The more pronounced effects of lithium in patients compared to controls suggest a disease-specific effect of this drug.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Bipolar disorder; Gene expression; Lithium; Lymphoblastoid cell lines; Morningness.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. and ECNP. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
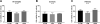
Similar articles
-
Lithium-induced gene expression alterations in two peripheral cell models of bipolar disorder.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Jul;20(6):462-475. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2017.1396357. Epub 2017 Nov 27. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29067888
-
RNA sequencing of bipolar disorder lymphoblastoid cell lines implicates the neurotrophic factor HRP-3 in lithium's clinical efficacy.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Jul;20(6):449-461. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2017.1372629. Epub 2017 Sep 22. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 28854847
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) expression is up-regulated in lymphoblastoid cell lines of lithium responsive bipolar disorder patients.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Jul;73:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23619527
-
The role of Wnt signaling and its interaction with diverse mechanisms of cellular apoptosis in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Jan 15;35(1):11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.08.031. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 20828594 Review.
-
Gene-expression studies in understanding the mechanism of action of lithium.Expert Rev Neurother. 2012 Jan;12(1):93-7. doi: 10.1586/ern.11.184. Expert Rev Neurother. 2012. PMID: 22243047 Review.
Cited by
-
Lithium Ions as Modulators of Complex Biological Processes: The Conundrum of Multiple Targets, Responsiveness and Non-Responsiveness, and the Potential to Prevent or Correct Dysregulation of Systems during Aging and in Disease.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 25;14(8):905. doi: 10.3390/biom14080905. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunomodulatory effect of lithium as a mechanism of action in bipolar disorder.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 17;17:1213766. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1213766. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37662097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanisms of Lithium Action: The Old and New Findings.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;18(4):467. doi: 10.3390/ph18040467. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-aging effects of lithium in lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with bipolar disorder and controls.J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Sep;128:38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.05.022. Epub 2020 May 26. J Psychiatr Res. 2020. PMID: 32516629 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Biomarkers in Bipolar Disorder and Response to Mood Stabilizers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 13;24(12):10067. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210067. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alda M, Grof P, Rouleau GA, Turecki G, Young LT. Investigating responders to lithium prophylaxis as a strategy for mapping susceptibility genes for bipolar disorder. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry. 2005;29:1038–1045. - PubMed
-
- Backlund L, Nikamo P, Hukic DS, Ek IR, Traskman-Bendz L, Landen M, Edman G, Schalling M, Frisen L, Osby U. Cognitive manic symptoms associated with the P2RX7 gene in bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorders. 2011;13:500–508. - PubMed
-
- Benes FM, Matzilevich D, Burke RE, Walsh J. The expression of proapoptosis genes is increased in bipolar disorder, but not in schizophrenia. Molecular psychiatry. 2006;11:241–251. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

