Resistant Hypertension, Time-Updated Blood Pressure Values and Renal Outcome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 28939716
- PMCID: PMC5634309
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006745
Resistant Hypertension, Time-Updated Blood Pressure Values and Renal Outcome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Apparent treatment resistant hypertension (aTRH) is highly prevalent in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) and entails worse cardiovascular prognosis. The impact of aTRH and long-term achievement of recommended blood pressure (BP) values on renal outcome remains largely unknown. We assessed the role of aTRH and BP on the development of chronic kidney disease in patients with T2D and hypertension in real-life clinical practice.
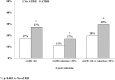
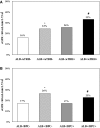
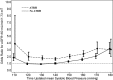
Methods and results: Clinical records from a total of 29 923 patients with T2D and hypertension, with normal baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate and regular visits during a 4-year follow-up, were retrieved and analyzed. The association between time-updated BP control (ie, 75% of visits with BP <140/90 mm Hg) and the occurrence of estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 and/or a reduction ≥30% from baseline was assessed. At baseline, 17% of patients had aTRH. Over the 4-year follow-up, 19% developed low estimated glomerular filtration rate and 12% an estimated glomerular filtration rate reduction ≥30% from baseline. Patients with aTRH showed an increased risk of developing both renal outcomes (adjusted odds ratio, 1.31 and 1.43; P<0.001 respectively), as compared with those with non-aTRH. No association was found between BP control and renal outcomes in non-aTRH, whereas in aTRH, BP control was associated with a 30% (P=0.036) greater risk of developing the renal end points.
Conclusions: ATRH entails a worse renal prognosis in T2D with hypertension. BP control is not associated with a more-favorable renal outcome in aTRH. The relationship between time-updated BP and renal function seems to be J-shaped, with optimal systolic BP values between 120 and 140 mm Hg.
Keywords: albuminuria; blood pressure; chronic kidney disease; diabetes (kidney); glomerular filtration rate; resistant hypertension.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures



References
-
- Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL. Resistant hypertension: an overview of evaluation and treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1749–1757. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, Ferdinand K, Giles TD, Falkner B, Carey RM; American Heart Association Professional Education Committee . Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2008;117:e510–e526. - PubMed
-
- De Nicola L, Gabbai FB, Agarwal R, Chiodini P, Borrelli S, Bellizzi V, Nappi F, Conte G, Minutolo R. Prevalence and prognostic role of resistant hypertension in chronic kidney disease patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:2461–2467. - PubMed
-
- Wolley MJ, Stowasser M. Resistant hypertension and chronic kidney disease: a dangerous liaison. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016;18:36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

