Lys63-polyubiquitination by the E3 ligase casitas B-lineage lymphoma-b (Cbl-b) modulates peripheral regulatory T cell tolerance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 28940360
- PMCID: PMC5721239
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13054
Lys63-polyubiquitination by the E3 ligase casitas B-lineage lymphoma-b (Cbl-b) modulates peripheral regulatory T cell tolerance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
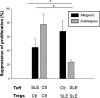
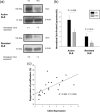
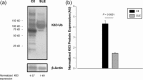
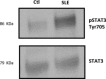
T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients display a wide array of anomalies in peripheral immune tolerance mechanisms. The role of ubiquitin ligases such as Cbl-b has been described recently in these phenomena. However, its role in resistance to suppression phenotype in SLE has not been characterized, which was the aim of the present study. Thirty SLE patients (20 with active disease and 10 with complete remission) and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were recruited. Effector (CD4+ CD25- ) and regulatory (CD4+ CD25+ ) T cells (Tregs ) were purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by magnetic selection. Suppression assays were performed in autologous and allogeneic co-cultures and analysed by a flow cytometry assay. Cbl-b expression and lysine-63 (K63)-specific polyubiquitination profile were assessed by Western blotting. We found a defective Cbl-b expression in Tregs from lupus patients in contrast to healthy controls (1·1 ± 0·9 versus 2·5 ± 1·8, P = 0·003), which was related with resistance to suppression (r = 0·633, P = 0·039). Moreover, this feature was associated with deficient K63 polyubiquitination substrates and enhanced expression of phosphorylated signal transducer and activation of transcription 3 (pSTAT-3) in Tregs from lupus patients. Our findings support that Cbl-b modulates resistance to suppression by regulating the K63 polyubiquitination profile in lupus Tregs . In addition, defective K63 polyubiquitination of STAT-3 is related to increased pSTAT-3 expression, and might promote the loss of suppressive capacity of Tregs in lupus patients.
Keywords: Cbl-b; K63-polyubiquitination; regulatory T cells; resistance to suppression; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2017 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of anergy-related factors involved in regulatory T cells defects in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients: Rapamycin and Vitamin D efficacy in restoring regulatory T cells.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Dec;19(12):1294-1303. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12509. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25351606
-
Casitas B lineage lymphoma b is a key regulator of peripheral tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Apr;65(4):1032-42. doi: 10.1002/art.37833. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23280105
-
Aberrant GITR expression on different T cell subsets and the regulation by glucocorticoid in systemic lupus erythematosus.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Feb;19(2):199-204. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12451. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25293713
-
Regulation of peripheral T cell tolerance by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b.Semin Immunol. 2007 Jun;19(3):206-14. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.004. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17391982 Review.
-
The Regulatory T Cell in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 18;10:159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00159. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30833946 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
STAT3 Interactors as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 16;19(6):1787. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061787. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29914167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating molecular markers linked to acute myocardial infarction and cuproptosis: bioinformatics analysis and validation in the AMI mice model.PeerJ. 2024 May 29;12:e17280. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17280. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38827298 Free PMC article.
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases as Immunotherapeutic Target in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Jun 5;7:106. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00106. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32582770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
K63 ubiquitination in immune signaling.Trends Immunol. 2022 Feb;43(2):148-162. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.12.005. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Trends Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35033428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deubiquitylating enzymes: potential target in autoimmune diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Dec;29(6):1683-1699. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00890-z. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34792672 Review.
References
-
- Fazekas de St Groth B, Zhu E, Asad S, Lee L. Flow cytometric detection of human regulatory T cells. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 707:263–79. - PubMed
-
- Miyara M, Sakaguchi S. Human FoxP3(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells: their knowns and unknowns. Immunol Cell Biol 2011; 89:346–51. - PubMed
-
- Rubtsov YP, Rasmussen JP, Chi EY et al Regulatory T cell‐derived interleukin‐10 limits inflammation at environmental interfaces. Immunity 2008; 28:546–58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

