Improved quantitative 90 Y bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT reconstruction with Monte Carlo scatter modeling
- PMID: 28940483
- PMCID: PMC5734647
- DOI: 10.1002/mp.12597
Improved quantitative 90 Y bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT reconstruction with Monte Carlo scatter modeling
Abstract
Purpose: In 90 Y microsphere radioembolization (RE), accurate post-therapy imaging-based dosimetry is important for establishing absorbed dose versus outcome relationships for developing future treatment planning strategies. Additionally, accurately assessing microsphere distributions is important because of concerns for unexpected activity deposition outside the liver. Quantitative 90 Y imaging by either SPECT or PET is challenging. In 90 Y SPECT model based methods are necessary for scatter correction because energy window-based methods are not feasible with the continuous bremsstrahlung energy spectrum. The objective of this work was to implement and evaluate a scatter estimation method for accurate 90 Y bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT imaging.
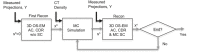
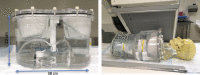
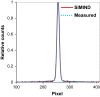
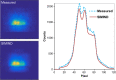
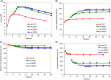
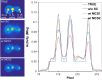
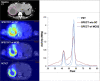
Methods: Since a fully Monte Carlo (MC) approach to 90 Y SPECT reconstruction is computationally very demanding, in the present study the scatter estimate generated by a MC simulator was combined with an analytical projector in the 3D OS-EM reconstruction model. A single window (105 to 195-keV) was used for both the acquisition and the projector modeling. A liver/lung torso phantom with intrahepatic lesions and low-uptake extrahepatic objects was imaged to evaluate SPECT/CT reconstruction without and with scatter correction. Clinical application was demonstrated by applying the reconstruction approach to five patients treated with RE to determine lesion and normal liver activity concentrations using a (liver) relative calibration.
Results: There was convergence of the scatter estimate after just two updates, greatly reducing computational requirements. In the phantom study, compared with reconstruction without scatter correction, with MC scatter modeling there was substantial improvement in activity recovery in intrahepatic lesions (from > 55% to > 86%), normal liver (from 113% to 104%), and lungs (from 227% to 104%) with only a small degradation in noise (13% vs. 17%). Similarly, with scatter modeling contrast improved substantially both visually and in terms of a detectability index, which was especially relevant for the low uptake extrahepatic objects. The trends observed for the phantom were also seen in the patient studies where lesion activity concentrations and lesion-to-liver concentration ratios were lower for SPECT without scatter correction compared with reconstruction with just two MC scatter updates: in eleven lesions the mean uptake was 4.9 vs. 7.1 MBq/mL (P = 0.0547), the mean normal liver uptake was 1.6 vs. 1.5 MBq/mL (P = 0.056) and the mean lesion-to-liver uptake ratio was 2.7 vs. 4.3 (P = 0.0402) for reconstruction without and with scatter correction respectively.
Conclusions: Quantitative accuracy of 90 Y bremsstrahlung imaging can be substantially improved with MC scatter modeling without significant degradation in image noise or intensive computational requirements.
Keywords: 90Y; SPECT/CT; bremsstrahlung; radioembolization; reconstruction.
© 2017 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radioembolization lung shunt estimation based on a 90 Y pretreatment procedure: A phantom study.Med Phys. 2018 Oct;45(10):4744-4753. doi: 10.1002/mp.13168. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 30179259
-
Quantitative Monte Carlo-based 90Y SPECT reconstruction.J Nucl Med. 2013 Sep;54(9):1557-63. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.119131. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 23907758
-
A deep neural network for fast and accurate scatter estimation in quantitative SPECT/CT under challenging scatter conditions.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 Dec;47(13):2956-2967. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04840-9. Epub 2020 May 15. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32415551 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Monte Carlo Algorithms to Cardiac Imaging Reconstruction.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(16):1960-1972. doi: 10.2174/1381612826999201228215225. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33371829 Review.
-
The impact of PET and SPECT on dosimetry for targeted radionuclide therapy.Z Med Phys. 2006;16(1):47-59. doi: 10.1078/0939-3889-00291. Z Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 16696370 Review.
Cited by
-
For Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Yttrium-90 Microspheres, Dose Volumetrics on Post-Treatment Bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT Predict Clinical Outcomes.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;15(3):645. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030645. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765603 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Tumor Control in 90Y Radioembolization by Logit Models with PET/CT-Based Dose Metrics.J Nucl Med. 2020 Jan;61(1):104-111. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.226472. Epub 2019 May 30. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 31147404 Free PMC article.
-
CT-free attenuation and Monte-Carlo based scatter correction-guided quantitative 90Y-SPECT imaging for improved dose calculation using deep learning.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Jul;52(9):3484-3499. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07191-5. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40080141 Free PMC article.
-
Standardizing SPECT/CT dosimetry following radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres.EJNMMI Phys. 2021 Oct 30;8(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s40658-021-00413-3. EJNMMI Phys. 2021. PMID: 34716850 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Spatial Concordance Between Theranostic Pairs Using Phantom and Patient-Specific Acceptance Criteria: Application to 99mTc-MAA SPECT/90Y-Microsphere PET.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Aug 1;104(5):1133-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 31022511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldsmith SJ. Radioimmunotherapy of lymphoma: Bexxar and Zevalin. Semin Nucl Med. 2010;40:122–135. - PubMed
-
- https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=90Y&Search=Search. Accessed January 28, 2017.
-
- Minarik D, Sjögreen Gleisner K, Ljungberg M. Evaluation of quantitative (90)Y SPECT based on experimental phantom studies. Phys Med Biol. 2008;53:5689–5703. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

