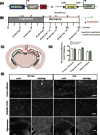
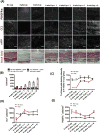
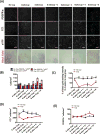
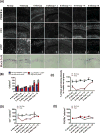
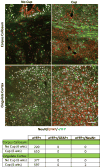
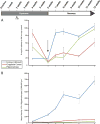
Lineage tracing reveals dynamic changes in oligodendrocyte precursor cells following cuprizone-induced demyelination
- PMID: 28940645
- PMCID: PMC5761347
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.23229
Lineage tracing reveals dynamic changes in oligodendrocyte precursor cells following cuprizone-induced demyelination
Abstract
The regeneration of oligodendrocytes is a crucial step in recovery from demyelination, as surviving oligodendrocytes exhibit limited structural plasticity and rarely form additional myelin sheaths. New oligodendrocytes arise through the differentiation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα) expressing oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) that are widely distributed throughout the CNS. Although there has been detailed investigation of the behavior of these progenitors in white matter, recent studies suggest that disease burden in multiple sclerosis (MS) is more strongly correlated with gray matter atrophy. The timing and efficiency of remyelination in gray matter is distinct from white matter, but the dynamics of OPCs that contribute to these differences have not been defined. Here, we used in vivo genetic fate tracing to determine the behavior of OPCs in gray and white matter regions in response to cuprizone-induced demyelination. Our studies indicate that the temporal dynamics of OPC differentiation varies significantly between white and gray matter. While OPCs rapidly repopulate the corpus callosum and mature into CC1 expressing mature oligodendrocytes, OPC differentiation in the cingulate cortex and hippocampus occurs much more slowly, resulting in a delay in remyelination relative to the corpus callosum. The protracted maturation of OPCs in gray matter may contribute to greater axonal pathology and disease burden in MS.
Keywords: demyelination; gray matter; multiple sclerosis; oligodendrocyte progenitor cells; remyelination.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bo L, Vedeler CA, Nyland H, Trapp BD, Mork SJ. Intracortical multiple sclerosis lesions are not associated with increased lymphocyte infiltration. Mult Scler. 2003;9:323–31. - PubMed
-
- Brink BP, Veerhuis R, Breij EC, van der Valk P, Dijkstra CD, Bo L. The pathology of multiple sclerosis is location-dependent: no significant complement activation is detected in purely cortical lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:147–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases