Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Vortioxetine Following Single- and Multiple-Dose Administration in Healthy Japanese Adults
- PMID: 28941196
- PMCID: PMC5900865
- DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.381
Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Vortioxetine Following Single- and Multiple-Dose Administration in Healthy Japanese Adults
Abstract
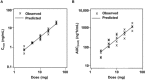
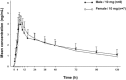
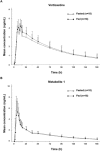
Three phase 1 randomized single-center studies assessed the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of vortioxetine after single- and multiple-dose administration in healthy Japanese adults. Study 1 assessed the pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine after administration of single rising doses to men and multiple doses to men and women; study 2 evaluated vortioxetine pharmacokinetics in elderly adults; and study 3 assessed food effects on vortioxetine pharmacokinetics in healthy men. The primary end points included pharmacokinetic parameters of vortioxetine and incidence of adverse events (AEs). Across all studies, 130 participants were randomized and 128 participants completed the studies. Vortioxetine was absorbed and eliminated from plasma slowly, and exposure to vortioxetine increased in an almost dose-proportional manner. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine or its metabolites were observed between the sexes in young and elderly adults. Study 3 demonstrated that vortioxetine and its metabolites had similar pharmacokinetics when administered in the fasted and fed states. Importantly, vortioxetine was safe and tolerated, with incidence of AEs comparable to that of placebo. No deaths or serious AEs leading to trial discontinuation were observed. Overall, vortioxetine pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability in Japanese adults were comparable to reports in non-Japanese populations.
Keywords: 5-HT; antidepressant; major depressive disorder; multimodal treatment; vortioxetine.
© 2017 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Vortioxetine in the Chinese Population.Adv Ther. 2019 Nov;36(11):3134-3146. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01092-4. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31552551 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of Effect of Vortioxetine on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ethanol, Diazepam, and Lithium.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016 Sep;55(9):1115-27. doi: 10.1007/s40262-016-0389-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016. PMID: 27048210 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intravenous vortioxetine to accelerate onset of effect in major depressive disorder: a 2-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019 Jul;34(4):153-160. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000271. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31094901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vortioxetine: Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Drug Interactions.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Jun;57(6):673-686. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0612-7. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29189941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vortioxetine: a novel antidepressant for the treatment of major depressive disorder.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019 Jan;14(1):81-89. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2019.1546691. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019. PMID: 30457395 Review.
Cited by
-
Vortioxetine vs. Other Antidepressants in Patients with Major Depressive Episode With or Without Substance Use Disorder.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(12):2296-2307. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210113150123. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33441069 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Vortioxetine in the Chinese Population.Adv Ther. 2019 Nov;36(11):3134-3146. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01092-4. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31552551 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and safety of vortioxetine in Japanese patients with major depressive disorder.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Feb;74(2):140-148. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12956. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31725942 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bioequivalence Study of Vortioxetine Hydrobromide Tablets in Healthy Chinese Subjects Under Fasting and Fed Conditions.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Sep 29;17:3035-3046. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S428771. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37795495 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adjunctive vortioxetine for SSRI-resistant major depressive disorder: a "real-world" chart review study.Braz J Psychiatry. 2020;42(3):317-321. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0690. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Braz J Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32159712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Mental health: Depression. 2016. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/. Accessed July 25, 2016.
-
- Gelenberg AJ. A review of the current guidelines for depression treatment. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(7):e15. - PubMed
-
- Henkel V, Seemuller F, Obermeier M, et al. Does early improvement triggered by antidepressants predict response/remission? Analysis of data from a naturalistic study on a large sample of inpatients with major depression. J Affect Disord. 2009;115(3):439–449. - PubMed
-
- Cassano P, Fava M. Tolerability issues during long‐term treatment with antidepressants. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2004;16(1):15–25. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg LD. Impact of drug tolerability on the selection of antidepressant treatment in patients with major depressive disorder. CNS Spectr. 2009;14(12 suppl 12):8–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

