ASF1a Promotes Non-homologous End Joining Repair by Facilitating Phosphorylation of MDC1 by ATM at Double-Strand Breaks
- PMID: 28943310
- PMCID: PMC5743198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.08.021
ASF1a Promotes Non-homologous End Joining Repair by Facilitating Phosphorylation of MDC1 by ATM at Double-Strand Breaks
Abstract
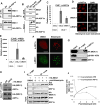
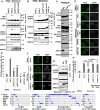
Double-strand breaks (DSBs) of DNA in eukaryotic cells are predominantly repaired by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). The histone chaperone anti-silencing factor 1a (ASF1a) interacts with MDC1 and is recruited to sites of DSBs to facilitate the interaction of phospho-ATM with MDC1 and phosphorylation of MDC1, which are required for the recruitment of RNF8/RNF168 histone ubiquitin ligases. Thus, ASF1a deficiency reduces histone ubiquitination at DSBs, decreasing the recruitment of 53BP1, and decreases NHEJ, rendering cells more sensitive to DSBs. This role of ASF1a in DSB repair cannot be provided by the closely related ASF1b and does not require its histone chaperone activity. Homozygous deletion of ASF1A is seen in 10%-15% of certain cancers, suggesting that loss of NHEJ may be selected in some malignancies and that the deletion can be used as a molecular biomarker for cancers susceptible to radiotherapy or to DSB-inducing chemotherapy.
Keywords: 53BP1; ASF1a; ATM; HR; MDC1; NHEJ; RNF168; RNF8; histone; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

