Neonatal Diabetes: Two Cases with Isolated Pancreas Agenesis due to Homozygous PTF1A Enhancer Mutations and One with Developmental Delay, Epilepsy, and Neonatal Diabetes Syndrome due to KCNJ11 Mutation
- PMID: 28943513
- PMCID: PMC5985387
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.5162
Neonatal Diabetes: Two Cases with Isolated Pancreas Agenesis due to Homozygous PTF1A Enhancer Mutations and One with Developmental Delay, Epilepsy, and Neonatal Diabetes Syndrome due to KCNJ11 Mutation
Abstract
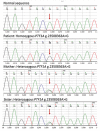
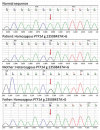
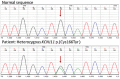
Neonatal diabetes mellitus is a rare form of monogenic diabetes which is diagnosed in the first six months of life. Here we report three patients with neonatal diabetes; two with isolated pancreas agenesis due to mutations in the pancreas-specific transcription factor 1A (PTF1A) enhancer and one with developmental delay, epilepsy, and neonatal diabetes (DEND) syndrome, due to a KCNJ11 mutation. The two cases with mutations in the distal enhancer of PTF1A had a homozygous g.23508363A>G and a homozygous g.23508437A>G mutation respectively. Previous functional analyses showed that these mutations can decrease expression of PTF1A which is involved in pancreas development. Both patients were born small for gestational age to consanguineous parents. Both were treated with insulin and pancreatic enzymes. One of these patients’ fathers was also homozygous for the PTF1A mutation, whilst his partner and the parents of the other patient were heterozygous carriers. In the case with DEND sydrome, a previosly reported heterozygous KCNJ11 mutation, p.Cys166Tyr (c.497G>A), was identified. This patient was born to nonconsanguineous parents with normal birth weight. The majority of neonatal diabetes patients with KCNJ11 mutations will respond to sulphonylurea treatment. Therefore Glibenclamide, an oral antidiabetic of the sulphonylurea group, was started. This treatment regimen relatively improved blood glucose levels and neurological symptoms in the short term. Because we could not follow the patient in the long term, we are not able to draw conclusions about the efficacy of the treatment. Although neonatal diabetes mellitus can be diagnosed clinically, genetic analysis is important since it is a guide for the treatment and for prognosis.
Keywords: Neonatal diabetes; PTF1A; pancreas agenesis; KCNJ11.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
