Celiac Disease: Diagnostic Standards and Dilemmas
- PMID: 28943611
- PMCID: PMC5548238
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases3020086
Celiac Disease: Diagnostic Standards and Dilemmas
Abstract
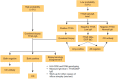
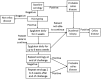
Celiac Disease (CD) affects at least 1% of the population and evidence suggests that prevalence is increasing. The diagnosis of CD depends on providers being alert to both typical and atypical presentations and those situations in which patients are at high risk for the disease. Because of variable presentation, physicians need to have a low threshold for celiac testing. Robust knowledge of the pathogenesis of this autoimmune disease has served as a catalyst for the development of novel diagnostic tools. Highly sensitive and specific serological assays including Endomysial Antibody (EMA), tissue transglutaminase (tTG), and Deamidated Gliadin Peptide (DGP) have greatly simplified testing for CD and serve as the foundation for celiac diagnosis. In addition, genetic testing for HLA DQ2 and DQ8 has become more widely available and there has been refinement of the gluten challenge for use in diagnostic algorithms. While diagnosis is usually straightforward, in special conditions including IgA deficiency, very young children, discrepant histology and serology, and adoption of a gluten free diet prior to testing, CD can be difficult to diagnose. In this review, we provide an overview of the history and current state of celiac disease diagnosis and provide guidance for evaluation of CD in difficult diagnostic circumstances.
Keywords: celiac disease; diagnosis; serology.
Conflict of interest statement
Dharmesh Kaswala and Gopal Veeraraghavan: None.
Ciaran Kelly: Consultant and scientific advisor related to Celiac disease for Alba, Alvine, Immunosan T and Pfizer.
Daniel Leffler: Consultant for/research support from: Alba Therapeutics, Alvine Pharmaceuticals, INOVA diagnostics, Genzyme, Coronado Biosciences, Pfizer, GI Supply.
Figures
References
-
- Maglio M., Florian F., Vecchiet M., Auricchio R., Paparo F., Spadaro R., Rapacciuolo L., Zanzi D., Franzese A., Sblattero D., et al. Majority of children with type 1 diabetes produce and deposit anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies in the small intestine. Diabetes. 2009;58:1578–1584. doi: 10.2337/db08-0962. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

