Sleeping site ecology, but not sex, affect ecto- and hemoparasite risk, in sympatric, arboreal primates (Avahi occidentalis and Lepilemur edwardsi)
- PMID: 28943886
- PMCID: PMC5607495
- DOI: 10.1186/s12983-017-0228-7
Sleeping site ecology, but not sex, affect ecto- and hemoparasite risk, in sympatric, arboreal primates (Avahi occidentalis and Lepilemur edwardsi)
Abstract
Background: A central question in evolutionary parasitology is to what extent ecology impacts patterns of parasitism in wild host populations. In this study, we aim to disentangle factors influencing the risk of parasite exposure by exploring the impact of sleeping site ecology on infection with ectoparasites and vector-borne hemoparasites in two sympatric primates endemic to Madagascar. Both species live in the same dry deciduous forest of northwestern Madagascar and cope with the same climatic constraints, they are arboreal, nocturnal, cat-sized and pair-living but differ prominently in sleeping site ecology. The Western woolly lemur (Avahi occidentalis) sleeps on open branches and frequently changes sleeping sites, whereas the Milne-Edward's sportive lemur (Lepilemur edwardsi) uses tree holes, displaying strong sleeping site fidelity. Sleeping in tree holes should confer protection from mosquito-borne hemoparasites, but should enhance the risk for ectoparasite infestation with mites and nest-adapted ticks. Sex may affect parasite risk in both species comparably, with males bearing a higher risk than females due to an immunosuppressive effect of higher testosterone levels in males or to sex-specific behavior. To explore these hypotheses, ectoparasites and blood samples were collected from 22 individuals of A. occidentalis and 26 individuals of L. edwardsi during the dry and rainy season.
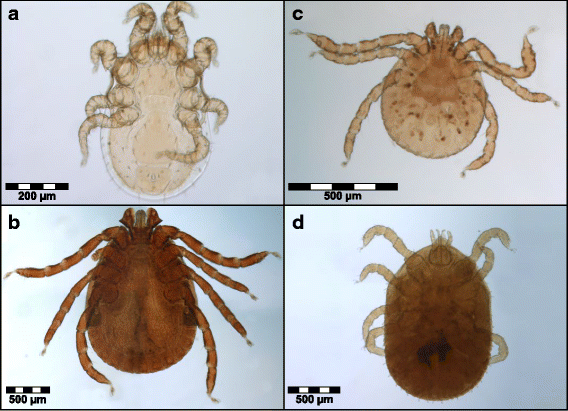
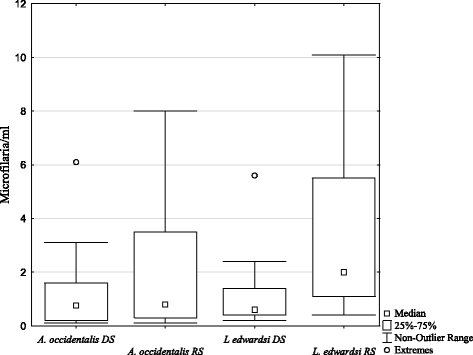
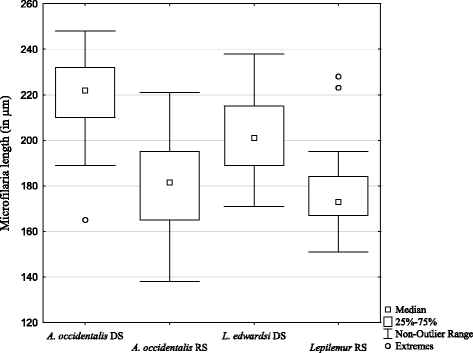
Results: L. edwardsi, but not A. occidentalis, harbored ectoparasites, namely ticks (Haemaphysalis lemuris [Ixodidae], Ornithodoros sp. [Argasidae]) and mites (Aetholaelaps trilyssa, [Laelapidae]), suggesting that sleeping in tree holes promotes infestation with ectoparasites. Interestingly, ectoparasites were found solely in the hot, rainy season with a prevalence of 75% (N = 16 animals). Blood smears were screened for the presence and infection intensity of hemoparasites. Microfilariae were detected in both species. Morphological characteristics suggested that each lemur species harbored two different filarial species. Prevalence of microfilarial infection was significantly lower in L. edwardsi than in A. occidentalis. No significant difference in infection intensity between the two host species, and no effect of season, daytime of sampling or sex on prevalence or infection intensity was found. In neither host species, parasite infection showed an influence on body weight as an indicator for body condition.
Conclusions: Our findings support that sleeping site ecology affects ectoparasite infestation in nocturnal, arboreal mammalian hosts in the tropics, whereas there is no significant effect of host sex. The influence of sleeping site ecology to vector-borne hemoparasite risk is less pronounced. The observed parasite infections did not affect body condition and thus may be of minor importance for shaping reproductive fitness. Findings provide first evidence for the specific relevance of sleeping site ecology on parasitism in arboreal and social mammals. Further, our results increase the sparse knowledge on ecological drivers of primate host-parasite interactions and transmission pathways in natural tropical environments.
Keywords: Behavior; Ecology; Madagascar; Microfilaria; Milne-Edward’s sportive lemur; Mites; Parasite; Primate; Seasonality; Sex; Sociality; Ticks; Tropics; Western woolly lemur.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All procedures were approved by the Ministère de l’Environnement, de l’Ecologie et des Forêts and Madagascar National Parks (MNP), and necessary research permits were obtained from the Malagasy authorities (License N° 167 /13/MEF/SG/DGF/DCB.SAP/SCB obtained on the 13th of July 2013 and N°072/14 obtained on the 12th of March 2014).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Heath A. Seasonality in ectoparasites. New Zeal Entomol. 1978;6:364–365. doi: 10.1080/00779962.1978.9722293. - DOI
-
- Kaiser M, Sutherst R, Bourne A, Gorissen L, Floyd R. Population dynamics of ticks on Ankole cattle in five ecological zones in Burundi and strategies for their control. Prev Vet Med. 1988;6:199–222. doi: 10.1016/0167-5877(88)90031-1. - DOI
-
- Gannon MR and Willig MR. Ecology of ectoparasites from tropical bats. Environm Entomol. 1995;24:1495–1503.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

