Downregulation of cytochrome c oxidase 1 induced radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28943930
- PMCID: PMC5604182
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6699
Downregulation of cytochrome c oxidase 1 induced radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
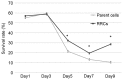
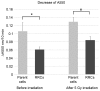
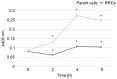
Comprehensive gene screening with transposons is a novel procedure for the systematic identification of resistant genes. The present study aimed to use this technique to identify candidate radioresistant genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. A transposon is a base sequence that can translocate to another location in the genome at random. By inserting the cytomegalovirus promotor as a transcriptional activator in the transposon, the following gene in the new location becomes overexpressed and the gene located at the transposon insertion site is downregulated. Consequently, various transposon-tagged cells, which have differentially overexpressed or downregulated genes using the transposon method can be obtained. Following the irradiation of transposon-tagged cells, candidate radioresistant genes can be selected in order to detect the location of the transposon in the cells that have survived. A total of 11 genes were detected as candidate radioresistant genes. Cytochrome c oxidase 1 (MT-CO1), an enzyme involved in apoptosis through the activation of the caspase cascade, was one of the candidate genes identified. The relative expression level of MT-CO1 was 0.12 in MT-CO1-downregulated cells which was significantly lower compared with the expression level in parent TE4 cells (P<0.001). The survival rate was 28.7% in MT-CO1-downregulated cells and 10.5% in parent TE4 cells 9 days following 5-Gy irradiation. The activity of cytochrome c and caspase-3 following irradiation was significantly lower in the MT-CO1-downregulated radioresistant cells compared with in TE4 cells. In conclusion, the novel gene screening technique demonstrated to be useful for detecting candidate radioresistant genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The results of the present study revealed that the downregulation of MT-CO1 induced radioresistance occurs by inhibiting the activation of the caspase cascade in radioresistant esophageal cancer cells.
Keywords: cytochrome c oxidase 1; esophageal cancer; gene screening; radioresistance; transposon.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive screening of genes resistant to an anticancer drug in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2015 Sep;47(3):867-74. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3085. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26202837 Free PMC article.
-
THUMP domain containing 2 protein possibly induces resistance to cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil in in vitro human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells as revealed by transposon activation mutagenesis.J Gene Med. 2019 Dec;21(12):e3135. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3135. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Gene Med. 2019. PMID: 31656051
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes related to radioresistance of human esophageal cancer cells.Chin J Cancer. 2010 Oct;29(10):882-8. doi: 10.5732/cjc.010.10148. Chin J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20868558
-
Single-cell RNA-seq of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line with fractionated irradiation reveals radioresistant gene expression patterns.BMC Genomics. 2019 Jul 25;20(1):611. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5970-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31345182 Free PMC article.
-
PTK7 regulates radioresistance through nuclear factor-kappa B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):14217-14224. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5288-3. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27557627
Cited by
-
Monocarboxylate Transporters 1 and 4 and MTCO1 in Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;13(9):2142. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092142. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946786 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel Carnobacterium maltaromaticum strains in bone marrow samples of patients with acute myeloid leukemia using a metagenomic binning approach.Int Microbiol. 2023 Nov;26(4):1033-1040. doi: 10.1007/s10123-023-00360-2. Epub 2023 Apr 22. Int Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37087535
References
-
- Ishida K, Ando N, Yamamoto S, Ide H, Shinoda M. Phase II study of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with concurrent radiotherapy in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: A Japan Esophageal Oncology Group (JEOG)/Japan Clinical Oncology Group trial (JCOG9516) Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004;34:615–619. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyh107. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fukuda K, Sakakura C, Miyagawa K, Kuriu Y, Kin S, Nakase Y, Hagiwara A, Mitsufuji S, Okazaki Y, Hayashizaki Y, Yamagishi H. Differential gene expression profiles of radioresistant oesophageal cancer cell lines established by continuous fractionated irradiation. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:1543–1550. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602187. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ogawa R, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura M, Mitsui A, Mori Y, Mori R, Tomoda K, Katada T, Harada K, Fujii Y. Identification of candidate genes involved in the radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells by microarray analysis. Dis Esophagus. 2008;21:288–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00759.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
