Increased expression of BPI fold-containing family A member 1 is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma
- PMID: 28943932
- PMCID: PMC5604161
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6662
Increased expression of BPI fold-containing family A member 1 is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma
Abstract
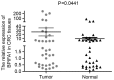
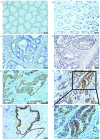
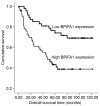
Bactericidal or permeability-increasing protein fold-containing family A member 1 (BPIFA1) has been demonstrated to be involved in inflammatory responses in the upper airway and the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. However, the expression levels of BPIFA1 and its clinical prognostic significance in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) has not yet been elucidated. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry were used to analyze the expression levels of BPIFA1 in CRC and normal mucosal tissues. The associations between BPIFA1 expression levels and clinicopathological characteristics, and its predictive value for prognosis in CRC, were statistically evaluated as appropriate. The expression levels of BPIFA1 were revealed to be upregulated at the transcriptional and translational levels in CRC tissues, compared with in normal mucosal tissues. A high expression level of BPIFA1 is significantly associated with invasion depth (P=0.040), lymph node metastasis (P=0.035) and distant metastasis (P=0.010). Furthermore, Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that BIPFA1 overexpression is associated with short survival time, and the Cox proportional hazards model of risk analysis indicated that BPIFA1 is an independent prognostic factor for patients with CRC. The results of the present study suggested that BPIFA1 expression is upregulated in CRC tissues, and that an increased expression level of BPIFA1 is associated with tumor invasion, metastasis and poor prognosis, indicating that BPIFA1 may be a potential clinical prognostic predictor and therapeutic target for patients with CRC.
Keywords: BPI fold-containing family A member 1; colorectal carcinoma; invasion; metastasis; prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of flavin-containing monooxygenase 5 predicts poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Mar;15(3):3923-3927. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.7724. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29456741 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR7 in colorectal carcinoma and its prognostic significance.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):13051-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26722500 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of PFTK1 in cancer cells predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jul;16(1):224-230. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6560. Epub 2017 May 10. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28498444
-
Association between KIAA1199 overexpression and tumor invasion, TNM stage, and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):2909-18. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045799 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal/Permeability-increasing protein fold-containing family member A1 in airway host protection and respiratory disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 May;52(5):525-34. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0297RT. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25265466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Type Catalog of Middle Turbinate Epithelium (Cell Catalog of Turbinate Epithelium).OTO Open. 2023 Dec 13;7(4):e91. doi: 10.1002/oto2.91. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. OTO Open. 2023. PMID: 38093720 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding seasonal weight loss tolerance in dairy goats: a transcriptomics approach.BMC Genomics. 2020 Sep 14;21(1):629. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06968-2. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32928114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernard W. Stewart CPW: World cancer report 2014: IARC. 2014
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
