Impact of positive ZEB1 expression in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma as an oncologic outcome-predicting indicator
- PMID: 28943941
- PMCID: PMC5592854
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6658
Impact of positive ZEB1 expression in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma as an oncologic outcome-predicting indicator
Abstract
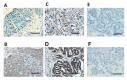
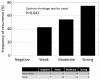
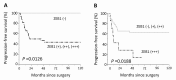
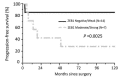
Several previous studies have revealed that the expression of zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) in solid malignancies has an important significance on the clinical outcome of patients. However, the association between ZEB1 expression and survival in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) remains unclear. The objective of the present study was to examine the extent of ZEB1 expression in EOC using immunohistochemical staining and investigate its association with patient outcome. A total of 40 patients with EOC initially treated with cytoreductive surgery and systematic chemotherapy were enrolled. ZEB1 expression was immunohistochemically categorized as negative, weak, moderate and strong according to the size of the staining area, and intensity. Subsequently, the associations between ZEB1 expression and recurrence/progression-free survival (RFS) rate were examined. The median age of patients in the current study was 54 years old (range, 22-72 years old). Among these patients, 15 (37.5%) exhibited International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage I disease, and 10 (25.0%), 13 (32.5%), and 2 (5%) had stage II, III, and IV disease, respectively. No patients with negative expression of ZEB1 experienced recurrence. In addition, ZEB1 expression was identified to be a significant predictor of a poorer RFS rate compared with negative expression (negative vs. weak, moderate and strong, P=0.0126). Furthermore, multivariate analyses revealed that moderate and strong ZEB1 expression levels were significant prognostic indicators of a poorer RFS rate in patients with EOC (hazard ratio, 2.265; 95% confidence interval, 1.072-8.021; P=0.0349). Confining analysis to patients with the clear-cell/mucinous histological type, those with moderate/strong ZEB1 expression demonstrated a significantly poorer RFS rate (P=0.0025). Positive ZEB1 expression may be an indicator to predict unfavorable RFS in patients with EOC.
Keywords: epithelial ovarian carcinoma; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; immunohistochemical staining; recurrence/progression-free survival; zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox factor 1 in epithelial ovarian cancer: A clinicopathological analysis of 238 patients.Mol Clin Oncol. 2016 Jan;4(1):18-22. doi: 10.3892/mco.2015.662. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26870350 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of ZEB1 leads to inversion of metastatic characteristics and restoration of paclitaxel sensitivity of chronic chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 10;8(59):99482-99494. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20107. eCollection 2017 Nov 21. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29245917 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-205 promotes motility of ovarian cancer cells via targeting ZEB1.Gene. 2015 Dec 15;574(2):330-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.017. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Gene. 2015. PMID: 26275944
-
The clinical role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell markers in advanced-stage ovarian serous carcinoma effusions.Hum Pathol. 2015 Jan;46(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Hum Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25455994
-
The utility of long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 as a prognostic biomarker in human solid tumors: A meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2018 Oct;485:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.06.018. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Clin Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29906419 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathologic Impact of NANOG, ZEB1, and EpCAM Biomarkers on Prognosis of Serous Ovarian Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Sep 1;24(9):3247-3259. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.9.3247. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37774079 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of connective tissue growth factor as a prognostic indicator and its possible involvement in the aggressive properties of epithelial ovarian carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2019 Dec;42(6):2323-2332. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7352. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31578579 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the tumor micro-environment in primary and metastatic tumors of different ovarian cancer histotypes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 24;11:1297219. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1297219. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38328306 Free PMC article.
-
Key Immunological Functions Involved in the Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Serous Carcinoma Discovered by the Gene Ontology-Based Immunofunctionome Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 24;19(11):3311. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113311. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30356023 Free PMC article.
-
KIF20A expression as a prognostic indicator and its possible involvement in the proliferation of ovarian clear‑cell carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jul;40(1):195-205. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6401. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29749467 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
