Role and mechanism of action of LRIG1 in ovarian cancer cell line and VP16 drug-resistant cell line
- PMID: 28943962
- PMCID: PMC5592861
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6730
Role and mechanism of action of LRIG1 in ovarian cancer cell line and VP16 drug-resistant cell line
Abstract
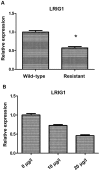
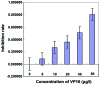
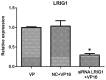
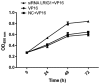
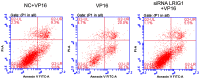
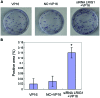
We investigated the role of leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains (LRIG)-1 in ovarian cancer cell line and VP16 drug-resistant cell line to explore the possible mechanism of action. Human ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3 and the VP16 drug-resistant cell line SKOV3/VP16 were used to investigate whether LRIG1 affects the sensitivity of SKOV3 to drugs. RT-qPCR was used to detect the difference in LRIG1 expression between drug-resistant and wild-type cell lines. siRNA LRIG1 was designed and transfected to silence LRIG1 to investigate the mechanism by which LRIG1 affects the sensitivity of SKOV3 to drugs. Wild-type cells were transfected with SKOV3. The cells were divided into 3 groups (VP16, NC + VP16 and siRNA LRIG1 + VP16 treatment group). VP16 (IC50 value) was added 24 h after transfection. The CCK-8 method was used to detect the proliferation of each group at multiple time points (0, 24, 48 and 72 h). A colony-forming assay was used to detect cell proliferation and flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis. The expression of LRIG1 was lower in the drug resistant cell line than that of the wild-type cell line. The expression of LRIG1 significantly decreased with the increase of VP16 concentration (P<0.05). The apoptotic rate was decreased but there was an increase on cell clones in the siLRIG1 + VP16-treated group as compared to VP16- and NC+ VP16-treated groups (P<0.05). The LRIG1 gene affects the sensitivity of SKOV3 cells to drug in a dose-related manner, indicating that the reduced expression of LRIG1 can inhibit cell apoptosis.
Keywords: SKO; VP16; cancer; drug resistance; leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1; ovarian.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased LRIG1 in Human Ovarian Cancer Cell SKOV3 Upregulates MRP-1 and Contributes to the Chemoresistance of VP16.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2016 May;31(4):125-32. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2015.1970. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2016. PMID: 27183435
-
[Gene therapy study on bladder cancer with recombinant adenoviral vector carrying LRIG1 gene driven by Survivin promoter].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;50(8):732-6. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23157908 Chinese.
-
[Biological effect of down-regulating of MTRR gene on cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells in vitro and in vivo studies].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;51(2):126-34. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2016.02.009. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26917482 Chinese.
-
[Molecular mechanism of LRIG1 cDNA-induced apoptosis in human glioma cell line H4].Ai Zheng. 2004 Oct;23(10):1149-54. Ai Zheng. 2004. PMID: 15473925 Chinese.
-
[Effect of XPG down-regulation gene expression towards the proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells and its chemosensitivity to platinum].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;47(4):286-91. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781116 Chinese.
References
-
- Krig SR, Frietze S, Simion C, Miller JK, Fry WH, Rafidi H, Kotelawala L, Qi L, Griffith OL, Gray JW, et al. Lrig1 is an estrogen-regulated growth suppressor and correlates with longer relapse-free survival in ERα-positive breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9:1406–1417. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0227. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lindström AK, Ekman K, Stendahl U, Tot T, Henriksson R, Hedman H, Hellberg D. LRIG1 and squamous epithelial uterine cervical cancer: Correlation to prognosis, other tumor markers, sex steroid hormones and smoking. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2008;18:312–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2007.01021.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
