Weight regain after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass has a large negative impact on the Bariatric Quality of Life Index
- PMID: 28944069
- PMCID: PMC5596836
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000153
Weight regain after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass has a large negative impact on the Bariatric Quality of Life Index
Abstract
Background: Despite initial successful weight loss, some patients may experience weight regain following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB).
Objective: To assess the impact of weight regain on bariatric patients' quality of life (QoL).
Methods: This was a prospective cross-sectional study. Fifty-six consecutive RYGB patients were recruited and divided into weight-regain and weight-stable cohorts. QoL was assessed using the Bariatric Quality of Life (BQL) questionnaire. The BQL Index scores of the weight-regain and weight-stable groups were compared using Student's t-test. Additionally, the BQL Index score of the weight-regain group was compared with that of historical prebariatric patients. Predictors of BQL were assessed using univariate and multivariate linear regression analyses.
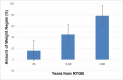
Results: Of 56 RYGB patients, 41 (73%) had weight regain. On average, patients had body mass index (BMI) of 37 ±7.5 kg/m2 and gained 34 ±26% of maximal weight initially lost. Weight-regain patients had lower BQL Index scores than weight-stable patients (44.8±6 vs 53±7, p<0.001). Patients with weight regain had similar BQL Index scores as the prebariatric patients despite lower BMI (BMI of 39.7±6.8 vs 47.2±7.6, p<0.05; BQL Index of 44.8±6 vs 41.6±10.4, p=0.144, respectively). Years from RYGB, BMI and amount of weight regain were associated with BQL Index on a univariate analysis (β=-0.55,-0.52, -0.7; p<0.0001). Only weight regain was a significant predictor of BQL on a multivariate analysis (β =-0.56; p=0.001).
Conclusion: Weight regain had a negative impact on bariatric patients' QoL. Patients who regained at least 15% of maximal weight lost appeared to have as low QoL as those who had not undergone bariatric surgery despite a lower BMI.
Keywords: BQL; HRQL; RYGB; bariatric surgery; quality of life; weight regain.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg 2013;23:427–36. doi:10.1007/s11695-012-0864-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khorgami Z, Shoar S, Andalib A, et al. . Trends in utilization of bariatric surgery, 2010-2014: sleeve gastrectomy dominates. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2017;13:774–8. doi:10.1016/j.soard.2017.01.031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ponce J, Nguyen NT, Hutter M, et al. . American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery estimation of bariatric surgery procedures in the United States, 2011-2014. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2015;11:1199–200. doi:10.1016/j.soard.2015.08.496 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dakin GF, Eid G, Mikami D, et al. . Endoluminal revision of gastric bypass for weight regain--a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2013;9:335–42. doi:10.1016/j.soard.2013.03.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brolin RE. Bariatric surgery and long-term control of morbid obesity. JAMA 2002;288:2793–6. doi:10.1001/jama.288.22.2793 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
