Enhanced biogas yield by thermo-alkali solubilization followed by co-digestion of intestine waste from slaughterhouse with food waste
- PMID: 28944152
- PMCID: PMC5591176
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-017-0936-x
Enhanced biogas yield by thermo-alkali solubilization followed by co-digestion of intestine waste from slaughterhouse with food waste
Abstract
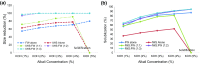
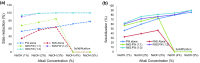
Intestine waste generated from slaughterhouse (IWS) is difficult to degrade in anaerobic process due to the presence of high protein and lipid contents. However, anaerobic co-digestion helps to increase the degradation of IWS by the addition of carbon-rich food waste (FW). To increase the biogas yield, thermo-alkali pretreatment may be more viable method for the anaerobic digestion of protein and lipid rich wastes. In the present study, Thermo-alkali pretreatment of intestine waste from slaughterhouse and food waste alone and mixing of IWS and FW with different ratios (1:1-1:3) on VS basis have been studied. To study the effect of Thermo-alkali pretreatment on solubilization of substrate, the substrate was mixed with alkali solutions (NaOH and KOH) at different concentrations of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5% solutions. The results revealed that the maximum solubilization was observed to be 94.7% and 90.1% at KOH (1:3 and 5%) and NaOH (1:3 and 5%), respectively. Based on the study, enhancement in biogas yield by 16% (IWS), 11.5% (FW), 12.2% (1:1), 18.11% (1:2) and 22.5% (1:3) in KOH pretreated waste when compared with NaOH pretreated waste.
Keywords: Biogas; Food waste; Intestine waste; Slaughterhouse; Solubilization; Thermo-alkali pretreatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahring BK (2003) Perspectives for Anaerobic Digestion. In: Biomethanation I. Part of the advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology book series (ABE), vol 81, pp 1–30 - PubMed
-
- Animut A, Meseret C, Egigu AK. Thermal and chemical pre-treatments of cow dung and poultry litter enhance biogas production in batch fermentation. Int J Sci Technol Res. 2014;3(11):165–170.
-
- APHA . Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20. Washington, DC: Am Publ Health Assoc; 1998.
-
- Belmonte M, Hsieh CF, Figueroa C, Campos JL, Vidal G. Effect of free ammonia nitrogen on the methanogenic activity of swine wastewater. Electron J Biotechnol. 2011;14(1):2.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

