Immunoreactivities of calbindin‑D28k, calretinin and parvalbumin in the somatosensory cortex of rodents during normal aging
- PMID: 28944879
- PMCID: PMC5865845
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7573
Immunoreactivities of calbindin‑D28k, calretinin and parvalbumin in the somatosensory cortex of rodents during normal aging
Abstract
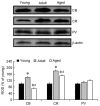
Calbindin‑D28k (CB), calretinin (CR) and parvalbumin (PV), which regulate cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations in neurons, are chemically expressed in γ‑aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic neurons that regulate the degree of glutamatergic excitation and output of projection neurons. The present study investigated age‑associated differences in CB, CR and PV immunoreactivities in the somatosensory cortex in three species (mice, rats and gerbils) of young (1 month), adult (6 months) and aged (24 months) rodents, using immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Abundant CB‑immunoreactive neurons were distributed in layers II and III, and age‑associated alterations in their number were different according to the species. CR‑immunoreactive neurons were not abundant in all layers; however, the number of CR‑immunoreactive neurons was the highest in all adult species. Many PV‑immunoreactive neurons were identified in all layers, particularly in layers II and III, and they increased in all layers with age in all species. The present study demonstrated that the distribution pattern of CB‑, CR‑ and PV‑containing neurons in the somatosensory cortex were apparently altered in number with normal aging, and that CB and CR exhibited a tendency to decrease in aged rodents, whereas PV tended to increase with age. These results indicate that CB, CR and PV are markedly altered in the somatosensory cortex, and this change may be associated with normal aging. These findings may aid the elucidation of the mechanisms of aging and geriatric disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of immunoreactivities of calbindin-D28k, calretinin and parvalbumin in the striatum between young, adult and aged mice, rats and gerbils.Neurochem Res. 2015 Apr;40(4):864-72. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1537-x. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25676337
-
The distribution of calbindinD-28k and parvalbumin immunoreactive neurons in the somatosensory area of the pigeon pallium.Anat Histol Embryol. 2018 Feb;47(1):64-70. doi: 10.1111/ahe.12325. Epub 2017 Nov 19. Anat Histol Embryol. 2018. PMID: 29152768
-
Immunocytochemical localization of calbindin-D28K, calretinin, and parvalbumin in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) visual cortex.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023;61(2):81-97. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2023.0010. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023. PMID: 37435896
-
[Age-related expression of calcium-binding proteins in autonomic ganglionic neurons].Adv Gerontol. 2016;29(2):247-253. Adv Gerontol. 2016. PMID: 28514541 Review. Russian.
-
Calcium-binding proteins in the human developing brain.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2002;165:III-IX, 1-92. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12236093 Review.
Cited by
-
Laminarin Attenuates Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Damage by Reducing Superoxide Anion Levels and Increasing Endogenous Antioxidants in the Dorsal Skin of Mice.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jun 30;18(7):345. doi: 10.3390/md18070345. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32629814 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Nervous System during Hibernation: Neuroprotective Strategies in Hypometabolic Conditions?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 13;20(9):2364. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092364. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31086053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calretinin and calbindin architecture of the midline thalamus associated with prefrontal-hippocampal circuitry.Hippocampus. 2021 Jul;31(7):770-789. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23271. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Hippocampus. 2021. PMID: 33085824 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Calbindin D28k Expression via Long-Term Alternate-Day Fasting Does Not Protect against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Focus on Delayed Neuronal Death, Gliosis and Immunoglobulin G Leakage.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 11;22(2):644. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020644. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33440708 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Reprogramming Ameliorates Aging Features in Dentate Gyrus Cells and Improves Memory in Mice.Stem Cell Reports. 2020 Nov 10;15(5):1056-1066. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.09.010. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Stem Cell Reports. 2020. PMID: 33096049 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

