DhHP‑6 attenuates cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion injury in rats through the inhibition of apoptosis
- PMID: 28944912
- PMCID: PMC5865850
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7569
DhHP‑6 attenuates cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion injury in rats through the inhibition of apoptosis
Abstract
As a novel reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger, deuterohemin His peptide‑6 (DhHP‑6) has been demonstrated to prolong the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans and has also exhibited protective effects in myocardial ischemia‑reperfusion injury. Whether similar effects occur during cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion (CIR) injury remains to be elucidated. The present study evaluated the function of DhHP‑6 and its underlying mechanisms in a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model in rats. The focal transient MCAO model was implemented using the Longa method of ischemia for 2 h followed by reperfusion for 22 h in male Wistar rats. DhHP‑6 was administered at the onset of reperfusion via intraperitoneal injection. The infarct volume, brain edema, brain apoptosis and neurological function were evaluated 24 h following stroke. To further determine the role of DhHP‑6 in CIR injury, the levels of ROS and malondialdehyde (MDA), the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH‑Px), and the protein expression levels of B‑cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‑2)‑associated X protein (Bax), cleaved caspase‑3, cytochrome c, Bcl‑2 and phosphorylated‑Akt/Akt were measured in ischemic cortex tissues. The results demonstrated that DhHP‑6 significantly improved infarct volume, brain edema and neurological deficits, and reduced the percentage of TUNEL‑positive cells. The levels of ROS and MDA were decreased, whereas no significant changes in the activities of SOD, CAT and GSH‑Px were observed. The levels of Bax, cleaved caspase‑3, and cytochrome c were downregulated, whereas the levels of Bcl‑2 and p‑Akt/Akt were upregulated. The results of the present study indicated that DhHP‑6 may offer therapeutic potential for cerebral ischemia. The neuroprotective effects of DhHP‑6 maybe mediated by its anti‑oxidative properties, anti‑apoptotic activities, or activation of the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/Akt survival pathway.
Figures

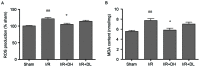




Similar articles
-
Acteoside Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats with Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(11):1645-1651. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00210. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 30381663
-
Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Mar 25;284:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29454613
-
Α‑lipoic acid protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2015 May;11(5):3659-65. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3170. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25572614
-
Liraglutide and its Neuroprotective Properties-Focus on Possible Biochemical Mechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease and Cerebral Ischemic Events.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 28;20(5):1050. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051050. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30823403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexamethasone and the prevention of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 15;765:179-95; discussion 196-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb16574.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 7486605 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Dipeptide, a Metabolite from Ambioba Secretion, Protects Cerebral Ischemia Injury by Blocking Apoptosis Via p-JNK/Bax Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 18;12:689007. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.689007. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34220513 Free PMC article.
-
The interrelationship between cerebral ischemic stroke and glioma: a comprehensive study of recent reports.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019 Oct 12;4:42. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0075-4. eCollection 2019. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019. PMID: 31637020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 Protects Against Apoptosis by Promoting Autophagy in the Oxygen Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion-Induced Injury.Front Neurol. 2019 Dec 5;10:1289. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01289. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31920915 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Involves MicroRNA-223 and the PTEN Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Dec 28;25:10077-10088. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919611. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31883264 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

