Neuroprotective effect of total flavonoids from Ilex pubescens against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 28944915
- PMCID: PMC5865877
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7540
Neuroprotective effect of total flavonoids from Ilex pubescens against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
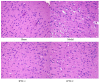
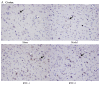
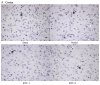
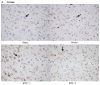
Ilex pubescens is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease and stroke. However, the underlying mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of Ilex pubescens total flavonoids (IPTF) on neuroprotection and the potential mechanisms in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Rats were pretreated with intragastric administration of IPTF at doses of 200 and 100 mg/kg for 5 days; middle cerebral artery occlusion surgery was then performed to induce cerebral I/R injury. Neurological deficits were determined using the 5‑point neurological function score evaluation system, brain infarct sizes were determined by 2,3,5‑triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining and alterations in brain histology were determined by hematoxylin and eosin staining. The neurological deficit score, the infarcted area and the brain tissue pathological injury were significantly reduced when the rats were pretreated with IPTF. In addition, inflammatory mediators and neurotrophic factors in the brain were investigated. IPTF pretreatment decreased the activities of total nitric oxide synthase (TNOS), induced NOS (iNOS) and constitutive NOS (cNOS), and the levels of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin‑1β (IL‑1β) and tumor necrosis factor‑α (TNF‑α), however, it increased the levels of IL‑10 in brain tissues. Furthermore, pretreatment with IPTF also increased the protein expressions of brain‑derived neurotrophic factor, glial cell‑derived neurotrophic factor and vascular endothelial growth factor, when compared with the model group. In conclusion, the results of the present study demonstrated that IPTF has a neuroprotective effect against focal cerebral I/R injury in rats. The mechanism may be associated with the decreased production of certain proinflammatory cytokines including NO, IL‑1β, TNF‑α, TNOS, iNOS and cNOS, the increased production of the anti‑inflammatory cytokine IL‑10 and the increased secretion of neurotrophic factors.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Ethanol extracts from Ilex pubescens promotes cerebral ischemic tolerance via modulation of TLR4-MyD88/TRIF signaling pathway in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jun 28;256:112680. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112680. Epub 2020 Feb 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32084554
-
Protective effect of Danhong Injection combined with Naoxintong Capsule on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;211:348-357. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28986333
-
Protective effect of Sheng-Nao-Kang decoction on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):228-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24161430
-
Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotective action of immunosuppressants--facts and hypotheses.J Cell Mol Med. 2004 Jan-Mar;8(1):45-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00259.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15090260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botanical flavonoids on coronary heart disease.Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(4):661-71. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X1100910X. Am J Chin Med. 2011. PMID: 21721147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomaterials for neuroengineering: applications and challenges.Regen Biomater. 2025 Feb 21;12:rbae137. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae137. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40007617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on the Potential Application of Herbal Medicine in Promoting Angiogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 19;13:928817. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.928817. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35928282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalein, Baicalin, and Wogonin: Protective Effects against Ischemia-Induced Neurodegeneration in the Brain and Retina.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jun 29;2021:8377362. doi: 10.1155/2021/8377362. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34306315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leonurine Reduces Oxidative Stress and Provides Neuroprotection against Ischemic Injury via Modulating Oxidative and NO/NOS Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 5;23(17):10188. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710188. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077582 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicines on Preclinical in vivo Models of Brain Ischemia-Reperfusion-Injury: Prospects for Neuroprotective Drug Discovery and Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 7;10:204. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00204. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30930774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu LP, Xu AD, Wong LK, Wang DZ, Wang YJ. and Expert consensus group of the evaluation & intervention of collateral circulation for ischemic stroke: Chinese consensus statement on the evaluation and intervention of collateral circulation for ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014;20:202–208. doi: 10.1111/cns.12226. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marmagkiolis K, Hakeem A, Cilingiroglu M, Gundogdu B, Iliescu C, Tsitlakidou D, Katramados A. Safety and efficacy of stent retrievers for the management of acute ischemic stroke: Comprehensive review and meta-analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:1758–1765. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2015.07.021. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

