Integration of Ion Mobility MSE after Fully Automated, Online, High-Resolution Liquid Extraction Surface Analysis Micro-Liquid Chromatography
- PMID: 28945354
- PMCID: PMC5677252
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03512
Integration of Ion Mobility MSE after Fully Automated, Online, High-Resolution Liquid Extraction Surface Analysis Micro-Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
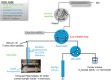
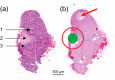
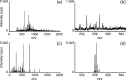
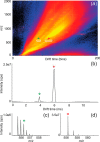
Direct analysis by mass spectrometry (imaging) has become increasingly deployed in preclinical and clinical research due to its rapid and accurate readouts. However, when it comes to biomarker discovery or histopathological diagnostics, more sensitive and in-depth profiling from localized areas is required. We developed a comprehensive, fully automated online platform for high-resolution liquid extraction surface analysis (HR-LESA) followed by micro-liquid chromatography (LC) separation and a data-independent acquisition strategy for untargeted and low abundant analyte identification directly from tissue sections. Applied to tissue sections of rat pituitary, the platform demonstrated improved spatial resolution, allowing sample areas as small as 400 μm to be studied, a major advantage over conventional LESA. The platform integrates an online buffer exchange and washing step for removal of salts and other endogenous contamination that originates from local tissue extraction. Our carry over-free platform showed high reproducibility, with an interextraction variability below 30%. Another strength of the platform is the additional selectivity provided by a postsampling gas-phase ion mobility separation. This allowed distinguishing coeluted isobaric compounds without requiring additional separation time. Furthermore, we identified untargeted and low-abundance analytes, including neuropeptides deriving from the pro-opiomelanocortin precursor protein and localized a specific area of the pituitary gland (i.e., adenohypophysis) known to secrete neuropeptides and other small metabolites related to development, growth, and metabolism. This platform can thus be applied for the in-depth study of small samples of complex tissues with histologic features of ∼400 μm or more, including potential neuropeptide markers involved in many diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, obesity, bulimia, and anorexia nervosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gas-phase separation of drugs and metabolites using modifier-assisted differential ion mobility spectrometry hyphenated to liquid extraction surface analysis and mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2013 Dec 17;85(24):11771-9. doi: 10.1021/ac4020353. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 24251629
-
Liquid extraction surface analysis mass spectrometry (LESA-MS) as a novel profiling tool for drug distribution and metabolism analysis: the terfenadine example.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2011 Dec 15;25(23):3587-96. doi: 10.1002/rcm.5274. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 22095508
-
A new approach to untargeted integration of high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data.Anal Chim Acta. 2013 Nov 1;801:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.09.028. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Anal Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 24139572
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
-
Quantitative profiling of folate and one-carbon metabolism in large-scale epidemiological studies by mass spectrometry.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45(12):1737-45. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2007.339. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007. PMID: 17963453 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Cell Metabolomics by Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1280:69-82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51652-9_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33791975
-
Ambient ionisation mass spectrometry for in situ analysis of intact proteins.J Mass Spectrom. 2018 Jul;53(7):565-578. doi: 10.1002/jms.4087. J Mass Spectrom. 2018. PMID: 29607564 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Anal Chem. 2025 Jul 29;97(29):15517-15549. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c05249. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40674148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein identification strategies in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry: a brief review.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2019 Feb;48:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.10.023. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 30476689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ mass spectrometry analysis of intact proteins and protein complexes from biological substrates.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):317-326. doi: 10.1042/BST20190793. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32010951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

