Airborne particulate matter increases MUC5AC expression by downregulating Claudin-1 expression in human airway cells
- PMID: 28946937
- PMCID: PMC5683821
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.10.100
Airborne particulate matter increases MUC5AC expression by downregulating Claudin-1 expression in human airway cells
Abstract
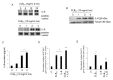
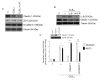
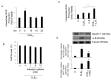
CLB2.0, a constituent of PM, induces secretion of multiple cytokines and chemokines that regulate airway inflammation. Specifically, IL-6 upregulates CLB2.0-induced MUC5AC and MUC1 expression. Interestingly, of the tight junction proteins examined, claudin-1 expression was inhibited by CLB2.0. While the overexpression of claudin-1 decreased CLB2.0-induced MUC5AC expression, it increased the expression of the anti-inflammatory mucin, MUC1. CLB2.0-induced IL-6 secretion was mediated by ROS. The ROS scavenger N-acetylcysteine inhibited CLB2.0-induced IL-6 secretion, thereby decreasing the CLB2.0-induced MUC5AC expression, whereas CLB2.0-induced MUC1 expression increased. CLB2.0 activated the ERK1/2 MAPK via a ROS-dependent pathway. ERK1/2 downregulated the claudin-1 and MUC1 expressions, whereas it dramatically increased CLB2.0-induced MUC5AC expression. These findings suggest that CLB2.0-induced ERK1/2 activation acts as a switch for regulating inflammatory conditions though a ROS-dependent pathway. Our data also suggest that secreted IL-6 regulates CLB2.0-induced MUC5AC and MUC1 expression via ROS-mediated downregulation of claudin-1 expression to maintain mucus homeostasis in the airway. [BMB Reports 2017; 50(10): 516-521].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin (IL) 36 gamma induces mucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming expression via IL-36 receptor-extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2, and p38-nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells in human airway epithelial cells.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018 Mar;32(2):87-93. doi: 10.1177/1945892418762844. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29644902
-
Arylhydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation in airway epithelial cells induces MUC5AC via reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Feb;24(1):133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.08.002. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 20709182
-
Effects of PM2.5 on mucus hypersecretion in airway through miR-133b-5p/EGFR/Claudin1/MUC5AC axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 26;16(10):8472-8483. doi: 10.18632/aging.205785. Epub 2024 May 26. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38809424 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin upregulates MUC5AC/B mucin gene expression in human airway epithelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 May 15;499(3):655-661. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.206. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29604272
-
Regulation of PMA-induced MUC5AC expression by heparin in human bronchial epithelial cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Jan;360(1-2):383-91. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1078-9. Epub 2011 Oct 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 21984036
Cited by
-
The Impact of PM2.5 on the Host Defense of Respiratory System.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Mar 4;8:91. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00091. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32195248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of ambient particulate matter and respiratory infections.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Mar;12(3):134-136. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.12.33. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32274073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of air pollutants in airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in asthma and COPD.Eur Respir Rev. 2022 Mar 23;31(163):210112. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0112-2021. Print 2022 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2022. PMID: 35321933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of intense exercise and pollution on the airways in a murine model.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2021 Mar 15;18(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12989-021-00401-6. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33722268 Free PMC article.
-
Health burden of sugarcane burning on agricultural workers and nearby communities.Inhal Toxicol. 2024 May;36(5):327-342. doi: 10.1080/08958378.2024.2316875. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Inhal Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38349733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Song KS. KATP channel controls LPS-induced MUC5AC overexpression in vivo. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;8:248–252.
-
- Valavanidis A, Fiotakis K, Vlachogianni T. Airborne particulate matter and human health: toxicological assessment and importance of size and composition of particles for oxidative damage and carcinogenic mechanisms. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2008;26:339–362. doi: 10.1080/10590500802494538. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

