Autonomous and non-autonomous roles for ephrin-B in interneuron migration
- PMID: 28947178
- PMCID: PMC5658245
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.09.024
Autonomous and non-autonomous roles for ephrin-B in interneuron migration
Abstract
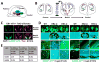
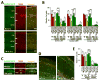
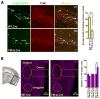
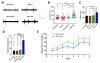
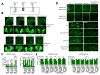
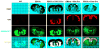
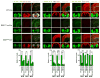
While several studies indicate the importance of ephrin-B/EphB bidirectional signaling in excitatory neurons, potential roles for these molecules in inhibitory neurons are largely unknown. We identify here an autonomous receptor-like role for ephrin-B reverse signaling in the tangential migration of interneurons into the neocortex using ephrin-B (EfnB1/B2/B3) conditional triple mutant (TMlz) mice and a forebrain inhibitory neuron specific Cre driver. Inhibitory neuron deletion of the three EfnB genes leads to reduced interneuron migration, abnormal cortical excitability, and lethal audiogenic seizures. Truncated and intracellular point mutations confirm the importance of ephrin-B reverse signaling in interneuron migration and cortical excitability. A non-autonomous ligand-like role was also identified for ephrin-B2 that is expressed in neocortical radial glial cells and required for proper tangential migration of GAD65-positive interneurons. Our studies thus define both receptor-like and ligand-like roles for the ephrin-B molecules in controlling the migration of interneurons as they populate the neocortex and help establish excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) homeostasis.
Keywords: Bidirectional signaling; EphB; Ephrin-B; Excitatory/inhibitory homeostasis; Inhibitory interneuron migration.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
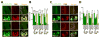
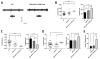
References
-
- Andrews W, Barber M, Hernadez-Miranda LR, Xian J, Rakic S, Sundaresan V, Rabbitts TH, Pannell R, Rabbitts P, Thompson H, Erskine L, Murakami F, Parnavelas JG. The role of Slit-Robo signaling in the generation, migration and morphological differentiation of cortical interneurons. Dev Biol. 2008;313:648–658. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.10.052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bennett KM, Afanador MD, Lal CV, Xu H, Persad E, Legan SK, Chenaux G, Dellinger M, Savani RC, Dravis C, Henkemeyer M, Schwarz MA. Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling increases alpha5beta1 integrin-mediated fibronectin deposition and reduces distal lung compliance. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;49:680–687. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0002OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Toth M. Fragile X mice develop sensory hyperreactivity to auditory stimuli. Neuroscience. 2001;103:1043–1050. S0306452201000367 [pii] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

