Polycomb complexes in X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 28947664
- PMCID: PMC5627167
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0021
Polycomb complexes in X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
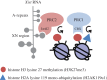
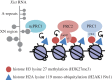
Identifying the critical RNA binding proteins (RBPs) that elicit Xist mediated silencing has been a key goal in X inactivation research. Early studies implicated the Polycomb proteins, a family of factors linked to one of two major multiprotein complexes, PRC1 and PRC2 (Wang 2001 Nat. Genet.28, 371-375 (doi:10.1038/ng574); Silva 2003 Dev. Cell4, 481-495 (doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00068-6); de Napoles 2004 Dev. Cell7, 663-676 (doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.005); Plath 2003 Science300, 131-135 (doi:10.1126/science.1084274)). PRC1 and PRC2 complexes catalyse specific histone post-translational modifications (PTMs), ubiquitylation of histone H2A at position lysine 119 (H2AK119u1) and methylation of histone H3 at position lysine 27 (H3K27me3), respectively, and accordingly, these modifications are highly enriched over the length of the inactive X chromosome (Xi). A key study proposed that PRC2 subunits bind directly to Xist RNA A-repeat element, a region located at the 5' end of the transcript known to be required for Xist mediated silencing (Zhao 2008 Science322, 750-756 (doi:10.1126/science.1163045)). Subsequent recruitment of PRC1 was assumed to occur via recognition of PRC2 mediated H3K27me3 by the CBX subunit of PRC1, as has been shown to be the case at other Polycomb target loci (Cao 2002 Science298, 1039-1043 (doi:10.1126/science.1076997)). More recently, several reports have questioned aspects of the prevailing view, both in relation to the mechanism for Polycomb recruitment by Xist RNA and the contribution of the Polycomb pathway to Xist mediated silencing. In this article I provide an overview of our recent progress towards resolving these discrepancies.This article is part of the themed issue 'X-chromosome inactivation: a tribute to Mary Lyon'.
Keywords: Polycomb; X inactivation; Xist RNA.
© 2017 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
I declare I have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

