ZNF516 suppresses EGFR by targeting the CtBP/LSD1/CoREST complex to chromatin
- PMID: 28947780
- PMCID: PMC5612949
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00702-5
ZNF516 suppresses EGFR by targeting the CtBP/LSD1/CoREST complex to chromatin
Abstract
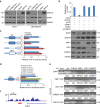
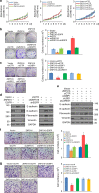
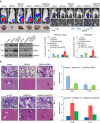
EGFR is required for animal development, and dysregulation of EGFR is critically implicated in malignant transformation. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the regulation of EGFR expression remains poorly explored. Here we report that the zinc-finger protein ZNF516 is a transcription repressor. ZNF516 is physically associated with the CtBP/LSD1/CoREST complex and transcriptionally represses a cohort of genes including EGFR that are critically involved in cell proliferation and motility. We demonstrate that the ZNF516-CtBP/LSD1/CoREST complex inhibits the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro and suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo. Significantly, low expression of ZNF516 is positively associated with advanced pathological staging and poor survival of breast carcinomas. Our data indicate that ZNF516 is a transcription repressor and a potential suppressor of EGFR, adding to the understanding of EGFR-related breast carcinogenesis and supporting the pursuit of ZNF516 as a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer. EGFR is a well-known oncogene; however, the mechanisms regulating its expression are still unclear. Here, analysing genome-wide chromatin associations, the authors show that in breast cancer cells ZNF516 represses EGFR transcription through the interaction with the CtBP/LSD1/CoREST complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
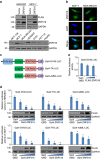
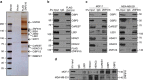
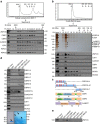
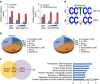


Similar articles
-
Endocrine resistance and breast cancer plasticity are controlled by CoREST.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022 Nov;29(11):1122-1135. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00856-x. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36344844 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin modifying complex CoREST/LSD1 negatively regulates notch pathway during cerebral cortex development.Dev Neurobiol. 2016 Dec;76(12):1360-1373. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22397. Epub 2016 May 31. Dev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27112428
-
SFMBT1 functions with LSD1 to regulate expression of canonical histone genes and chromatin-related factors.Genes Dev. 2013 Apr 1;27(7):749-66. doi: 10.1101/gad.210963.112. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23592795 Free PMC article.
-
CoREST-like complexes regulate chromatin modification and neuronal gene expression.J Mol Neurosci. 2006;29(3):227-39. doi: 10.1385/JMN:29:3:227. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17085781 Review.
-
CoREST in pieces: Dismantling the CoREST complex for cancer therapy and beyond.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 6;11(23):eads6556. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads6556. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40479062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PBMC gene expression profiles of female Bangladeshi adults chronically exposed to arsenic-contaminated drinking water.Environ Pollut. 2020 Apr;259:113672. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113672. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Environ Pollut. 2020. PMID: 31918125 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal of E1A binding protein 2 promotes the malignancy of osteosarcoma cells via JAK1/Stat3 signaling.J Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Mar;14(1):67-76. doi: 10.1007/s12079-019-00523-9. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 31214864 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the expression levels of lysine-specific demethylase 1 and survival outcomes between triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Feb;21(2):102. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12363. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33376535 Free PMC article.
-
De novo pyrimidine biosynthetic complexes support cancer cell proliferation and ferroptosis defence.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Jun;25(6):836-847. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01146-4. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37291265
-
LSD1 deficiency in breast cancer cells promotes the formation of pre-metastatic niches.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Nov 12;8(1):260. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00751-2. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39528717 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

