Detection and application of neurochemical profile by multiple regional 1H-MRS in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 28948086
- PMCID: PMC5607555
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.792
Detection and application of neurochemical profile by multiple regional 1H-MRS in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Introduction: The accurate diagnosis and monitoring of idiopathic Parkinson disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, has not been fully developed. This study sought to identify a neurochemical profile in multiple regions of the PD brain and healthy controls by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). We aimed to track changes of the brain neurochemical, quantify neuronal loss, and further determine the diagnostic value of 1H-MRS.
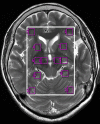
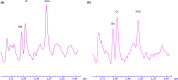
Methods: PD patients and healthy controls recruited from Second Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, southern China, underwent 1H-MRS. Chemical information was obtained for ratios of N-acetylaspartate to creatine (NAA/Cr), NAA to choline (NAA/Cho), and Cho to Cr for substantia nigra, globus pallidus, prefrontal lobe, hippocampus, cuneus gyrus, and dorsal thalamus regions.
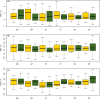
Results: Compared to the 20 healthy controls (12 male, age 58.75 ± 5.03 years), the 42 patients (21 male, age 61.60 ± 6.40 years) showed lower NAA/Cr and NAA/Cho ratios in substantia nigra, globus pallidus, prefrontal lobe, hippocampus, cuneus gyrus and dorsal thalamus regions (p < .01); NAA/Cr and NAA/Cho ratios were reduced for both patients with unilateral and mild/no cognitive impairment (p < .01); Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale score was inversely correlated with NAA/Cr ratios in the substantia nigra (r = -.32; p = .042).
Conclusion: NAA/Cr and NAA/Cho ratios may be useful metabolic biomarkers for early diagnosis of PD. Multi-voxel 1H-MRS can provide information on brain neurochemistry and may be a promising technique for diagnosis of and monitoring neuronal loss in PD.
Keywords: N‐acetylaspartate (NAA); Parkinson's disease; proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Figures
References
-
- Abe, K. , Terakawa, H. , Takanashi, M. , Watanabe, Y. , Tanaka, H. , Fujita, N. , … Yanagihara, T . (2000). Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of patients with parkinsonism. Brain Research Bulletin, 52, 589–595. - PubMed
-
- Choe, B.‐Y. , Park, J.‐W. , Lee, K.‐S. , Son, B.‐C. , Kim, M.‐C. , Kim, B.‐S. , … Shinn, K. S . (1998). Neuronal laterality in Parkinson's disease with unilateral symptom by in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Investigative Radiology, 33, 450–455. - PubMed
-
- Clarke, C. E. , & Lowry, M. (2000). Basal ganglia metabolite concentrations in idiopathic Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. European Journal of Neurology: The Official Journal of the European Federation of Neurological Societies, 7, 661. - PubMed
-
- Dalrymple‐Alford, J. C. , MacAskill, M. R. , Nakas, C. T. , Livingston, L. , Graham, C. , Crucian, G. P. , … Anderson, T. J . (2010). The MoCA: Well‐suited screen for cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology, 75, 1717–1725. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181fc29c9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dauer, W. , & Przedborski, S. (2003). Parkinson's disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron, 39, 889–909. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

