The complete chloroplast genome of Cinnamomum camphora and its comparison with related Lauraceae species
- PMID: 28948105
- PMCID: PMC5609524
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3820
The complete chloroplast genome of Cinnamomum camphora and its comparison with related Lauraceae species
Abstract
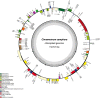
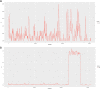
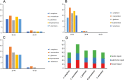
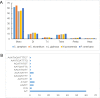
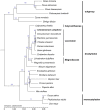
Cinnamomum camphora, a member of the Lauraceae family, is a valuable aromatic and timber tree that is indigenous to the south of China and Japan. All parts of Cinnamomum camphora have secretory cells containing different volatile chemical compounds that are utilized as herbal medicines and essential oils. Here, we reported the complete sequencing of the chloroplast genome of Cinnamomum camphora using illumina technology. The chloroplast genome of Cinnamomum camphora is 152,570 bp in length and characterized by a relatively conserved quadripartite structure containing a large single copy region of 93,705 bp, a small single copy region of 19,093 bp and two inverted repeat (IR) regions of 19,886 bp. Overall, the genome contained 123 coding regions, of which 15 were repeated in the IR regions. An analysis of chloroplast sequence divergence revealed that the small single copy region was highly variable among the different genera in the Lauraceae family. A total of 40 repeat structures and 83 simple sequence repeats were detected in both the coding and non-coding regions. A phylogenetic analysis indicated that Calycanthus is most closely related to Lauraceae, both being members of Laurales, which forms a sister group to Magnoliids. The complete sequence of the chloroplast of Cinnamomum camphora will aid in in-depth taxonomical studies of the Lauraceae family in the future. The genetic sequence information will also have valuable applications for chloroplast genetic engineering.
Keywords: Chloroplast genome; Cinnamomum camphora; Illumina sequencing; Lauraceae; Phylogeny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Babu KN, Sajina A, Minoo D, John CZ, Mini PM, Tushar KV, Rema J, Ravindran PN. Micropropagation of camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora) Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture. 2003;74:179–183.
-
- Bremer B, Bremer K, Chase M, Fay M, Reveal J, Soltis D, Soltis P, Stevens P. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 2009;161(2):105–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8339.2009.00996.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

