NCS-Rapgef2, the Protein Product of the Neuronal Rapgef2 Gene, Is a Specific Activator of D1 Dopamine Receptor-Dependent ERK Phosphorylation in Mouse Brain
- PMID: 28948210
- PMCID: PMC5611689
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0248-17.2017
NCS-Rapgef2, the Protein Product of the Neuronal Rapgef2 Gene, Is a Specific Activator of D1 Dopamine Receptor-Dependent ERK Phosphorylation in Mouse Brain
Erratum in
-
Correction: Jiang et al., NCS-Rapgef2, the Protein Product of the Neuronal Rapgef2 Gene, Is a Specific Activator of D1 Dopamine Receptor-Dependent ERK Phosphorylation in Mouse Brain (eNeuro September/October 2017, 4(5) e0248-17.2017 1-17 https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0248-17.2017).eNeuro. 2018 Oct 15;5(5):ENEURO.0379-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0379-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30406181 Free PMC article.
Abstract
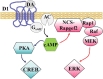
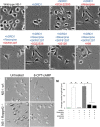
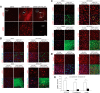
The neuritogenic cAMP sensor (NCS), encoded by the Rapgef2 gene, links cAMP elevation to activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Transducing human embryonic kidney (HEK)293 cells, which do not express Rapgef2 protein or respond to cAMP with ERK phosphorylation, with a vector encoding a Rapgef2 cDNA reconstituted cAMP-dependent ERK activation. Mutation of a single residue in the cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (CNBD) conserved across cAMP-binding proteins abrogated cAMP-ERK coupling, while deletion of the CNBD altogether resulted in constitutive ERK activation. Two types of mRNA are transcribed from Rapgef2 in vivo. Rapgef2 protein expression was limited to tissues, i.e., neuronal and endocrine, expressing the second type of mRNA, initiated exclusively from an alternative first exon called here exon 1', and an alternative 5' protein sequence leader fused to a common remaining open reading frame, which is termed here NCS-Rapgef2. In the male mouse brain, NCS-Rapgef2 is prominently expressed in corticolimbic excitatory neurons, and striatal medium spiny neurons (MSNs). Rapgef2-dependent ERK activation by the dopamine D1 agonist SKF81297 occurred in neuroendocrine neuroscreen-1 (NS-1) cells expressing the human D1 receptor and was abolished by deletion of Rapgef2. Corticolimbic [e.g., dentate gyrus (DG), basolateral amygdala (BLA)] ERK phosphorylation induced by SKF81297 was significantly attenuated in CamK2α-Cre+/- ; Rapgef2cko/cko male mice. ERK phosphorylation in nucleus accumbens (NAc) MSNs induced by treatment with SKF81297, or the psychostimulants cocaine or amphetamine, was abolished in male Rapgef2cko/cko mice with NAc NCS-Rapgef2-depleting AAV-Synapsin-Cre injections. We conclude that D1-dependent ERK phosphorylation in mouse brain requires NCS-Rapgef2 expression.
Keywords: GPCR; MAP kinase; amphetamine; cAMP; cell signaling; cocaine; psycho-stimulants.
Figures




References
-
- Bertran-Gonzalez J, Bosch C, Maroteaux M, Matamales M, Herve D, Valjent E, Girault JA (2008) Opposing patterns of signaling activation in dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing striatal neurons in response to cocaine and haloperidol. J Neurosci 28:5671–5685. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1039-08.2008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
