Economics of open tibial fractures: the pivotal role of length-of-stay and infection
- PMID: 28948497
- PMCID: PMC5612906
- DOI: 10.1186/s13561-017-0168-0
Economics of open tibial fractures: the pivotal role of length-of-stay and infection
Abstract
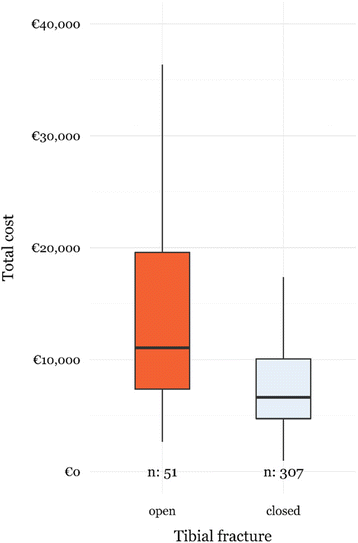
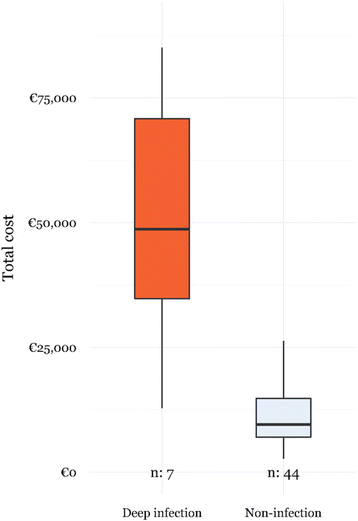
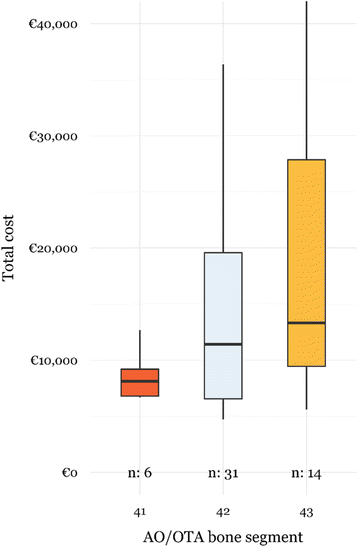
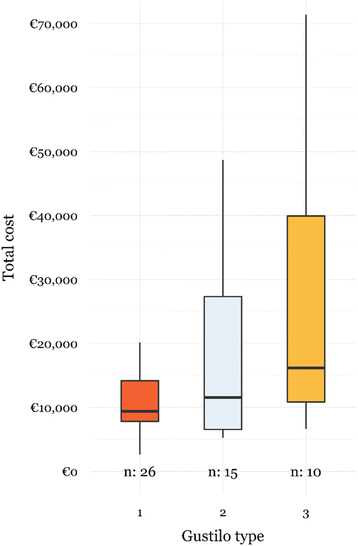
In order to define strategies to curb the continuing increase in healthcare costs, we describe the cost breakdown of open tibial fractures. Twenty-seven clinical and process variables were recorded retrospectively, and five main hospital related cost categories were defined. Three multivariate linear models were fitted to the data. Total healthcare costs of open tibial fractures were almost twice as high compared to closed fractures and mainly existed of hospitalization costs. Length-of-stay (LOS) was found to be the most important variable driving the healthcare costs of open tibial fractures. Deep infection lead to a 6-fold increase of LOS and 5-fold increase in total healthcare costs of open tibial fractures. Therefore, appropriate international consensus guidelines are required to improve not only the patient outcome (infection prevention) but also reduce overall healthcare cost by focusing on reducing the LOS.
Keywords: Costs analysis; Healthcare financing; Open tibial fractures.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- OECD. (n.d.). OECD Statistics. Health expenditure and financing. Retrieved June 1, 2016, from http://stats.oecd.org/index.aspx.
-
- OECD Health Statistics. WHO Global Health Expenditure Database; 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/health-data-en. - DOI
-
- Smeets B, Nijs S, Nderlita M, Vandoren C, Hoekstra H. Health Care Usage and Related Costs in Fibular Plating for AO Type 44-B Ankle Fractures in a Belgian University Hospital: An Exploratory Analysis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2016.02.004. - PubMed
-
- Papakostidis C, Kanakaris NK, Pretel J, Faour O, Morell DJ, Giannoudis PV. Prevalence of complications of open tibial shaft fractures stratified as per the Gustilo-Anderson classification. Injury. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2011.10.015. - PubMed
-
- Metsemakers WJ, Handojo K, Reynders P, Sermon A, Vanderschot P, Nijs S. Individual risk factors for deep infection and compromised fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures: A single centre experience of 480 patients. Injury. 2015;46(4):740–745. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2014.12.018. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

