The α2A -adrenoceptor suppresses excitatory synaptic transmission to both excitatory and inhibitory neurons in layer 4 barrel cortex
- PMID: 28948610
- PMCID: PMC5685826
- DOI: 10.1113/JP275142
The α2A -adrenoceptor suppresses excitatory synaptic transmission to both excitatory and inhibitory neurons in layer 4 barrel cortex
Abstract
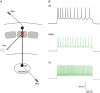
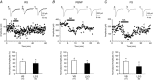
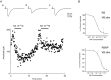
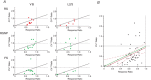
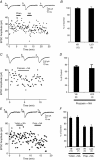
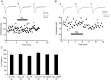
Key points: The effects of noradrenaline on excitatory synaptic transmission to regular spiking (excitatory) cells as well as regular spiking non-pyramidal and fast spiking (both inhibitory) cells in cortical layer 4 were studied in thalamocortical slice preparations, focusing on vertical input from thalamus and layer 2/3 in the mouse barrel cortex. Excitatory synaptic responses were suppressed by noradrenaline. However, currents induced by iontophoretically applied glutamate were not suppressed. Further, paired pulse ratio and coefficient of variation analysis indicated the site of action was presynaptic. Pharmacological studies indicated that the suppression was mediated by the α2- adrenoceptor. Consistent with this, involvement of α2A -adrenoceptor activation in the synaptic suppression in excitatory and inhibitory cells was confirmed by the use of α2A -adrenoceptor knockout mice.
Abstract: The mammalian neocortex is widely innervated by noradrenergic (NA) fibres from the locus coeruleus. To determine the effects of NA on vertical synaptic inputs to layer 4 (L4) cells from the ventrobasal thalamus and layer 2/3 (L2/3), thalamocortical slices were prepared and whole-cell recordings were made from L4 cells. Excitatory synaptic responses were evoked by electrical stimulation of the thalamus or L2/3 immediately above. Recorded cells were identified as regular spiking, regular spiking non-pyramidal or fast spiking cells through their firing patterns in response to current injections. NA suppressed (∼50% of control) excitatory vertical inputs to all cell types in a dose-dependent manner. The presynaptic site of action of NA was suggested by three independent studies. First, responses caused by iontophoretically applied glutamate were not suppressed by NA. Second, the paired pulse ratio was increased during NA suppression. Finally, a coefficient of variation (CV) analysis was performed and the resultant diagonal alignment of the ratio of CV-2 plotted against the ratio of the amplitude of postsynaptic responses suggests a presynaptic mechanism for the suppression. Experiments with phenylephrine (an α1 -agonist), prazosin (an α1 -antagonist), yohimbine (an α2 -antagonist) and propranolol (a β-antagonist) indicated that suppression was mediated by the α2 -adrenoceptor. To determine whether the α2A -adrenoceptor subtype was involved, α2A -adrenoceptor knockout mice were used. NA failed to suppress EPSCs in all cell types, suggesting an involvement of the α2A -adrenoceptor. Altogether, we concluded that NA suppresses vertical excitatory synaptic connections in L4 excitatory and inhibitory cells through the presynaptic α2A -adrenoceptor.
Keywords: EPSC; alpha 2A-KO; mouse; noradrenaline; presynaptic inhibition; thalamocortical.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Agmon A & Connors BW (1991). Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience 41, 365–379. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG & Sinnamon HM (1977). The locus coeruleus: Neurobiology of a central noradrenergic nucleus. Prog Neurobiol 9, 147–196. - PubMed
-
- Aoki C, Go CG, Venkatesan C & Kurose H (1994). Perikaryal and synaptic localization of α2A‐adrenergic receptor‐like immunoreactivity. Brain Res 650, 181–204. - PubMed
-
- Aston‐Jones G & Cohen JD (2005). An integrative theory of locus coeruleus‐norepinephrine function: Adaptive gain and optical performance. Annu Rev Neurosci 28, 403–450. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM & Stevens CF (1990). Presynaptic mechanism for long‐term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 346, 724–729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

