Calcium influx through TRPV4 channels modulates the adherens contacts between retinal microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 28949006
- PMCID: PMC5685834
- DOI: 10.1113/JP275052
Calcium influx through TRPV4 channels modulates the adherens contacts between retinal microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
Key points: Endothelial cells employ transient receptor potential isoform 4 (TRPV4) channels to sense ambient mechanical and chemical stimuli. In retinal microvascular endothelial cells, TRPV4 channels regulate calcium homeostasis, cytoskeletal signalling and the organization of adherens junctional contacts. Intracellular calcium increases induced by TRPV4 agonists include a significant contribution from calcium release from internal stores. Activation of TRPV4 channels regulates retinal endothelial barriers in vitro and in vivo. TRPV4 sensing may provide a feedback mechanism between sensing shear flow and eicosanoid modulators, vascular permeability and contractility at the inner retinal endothelial barrier.
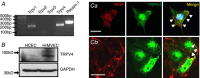
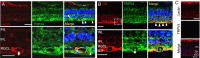
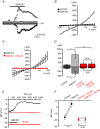
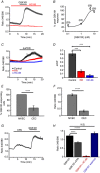
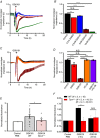
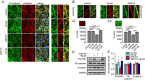
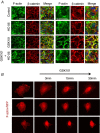
Abstract: The identity of microvascular endothelial (MVE) mechanosensors that sense blood flow in response to mechanical and chemical stimuli and regulate vascular permeability in the retina is unknown. Using immunohistochemistry, calcium imaging, electrophysiology, impedance measurements and vascular permeability assays, we show that the transient receptor potential isoform 4 (TRPV4) plays a major role in Ca2+ /cation signalling, cytoskeletal remodelling and barrier function in retinal microvasculature in vitro and in vivo. Human retinal MVE cells (HrMVECs) predominantly expressed Trpv1 and Trpv4 transcripts, and TRPV4 was broadly localized to the plasma membrane of cultured cells and intact blood vessels in the inner retina. Treatment with the selective TRPV4 agonist GSK1016790A (GSK101) activated a nonselective cation current, robustly elevated [Ca2+ ]i and reversibly increased the permeability of MVEC monolayers. This was associated with disrupted organization of endothelial F-actin, downregulated expression of occludin and remodelling of adherens contacts consisting of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin) and β-catenin. In vivo, GSK101 increased the permeability of retinal blood vessels in wild type but not in TRPV4 knockout mice. Agonist-evoked effects on barrier permeability and cytoskeletal reorganization were antagonized by the selective TRPV4 blocker HC 067047. Human choroidal endothelial cells expressed lower TRPV4 mRNA/protein levels and showed less pronounced agonist-evoked calcium signals compared to MVECs. These findings indicate a major role for TRPV4 in Ca2+ homeostasis and barrier function in human retinal capillaries and suggest that TRPV4 may differentially contribute to the inner vs. outer blood-retinal barrier function.
Keywords: TRPV4; adherens junctions; calcium; retinal microvascular endothelial cells; vascular permeability.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Akazawa Y, Yuki T, Yoshida H, Sugiyama Y & Inoue S (2013). Activation of TRPV4 strengthens the tight‐junction barrier in human epidermal keratinocytes. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 26, 15–21. - PubMed
-
- Berna‐Erro A, Izquierdo‐Serra M, Sepúlveda RV, Rubio‐Moscardo F, Doñate‐Macián P, Serra SA, Carrillo‐Garcia J, Perálvarez‐Marín A, González‐Nilo F, Fernández‐Fernández JM & Valverde MA (2017). Structural determinants of 5′,6′‐epoxyeicosatrienoic acid binding to and activation of TRPV4 channel. Sci Rep 7, 10522. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

