Development of an antibiotic marker-free platform for heterologous protein production in Streptomyces
- PMID: 28950904
- PMCID: PMC5615484
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-017-0781-y
Development of an antibiotic marker-free platform for heterologous protein production in Streptomyces
Abstract
Background: The industrial use of enzymes produced by microorganisms is continuously growing due to the need for sustainable solutions. Nevertheless, many of the plasmids used for recombinant production of proteins in bacteria are based on the use of antibiotic resistance genes as selection markers. The safety concerns and legal requirements surrounding the increased use of antibiotic resistance genes have made the development of new antibiotic-free approaches essential.
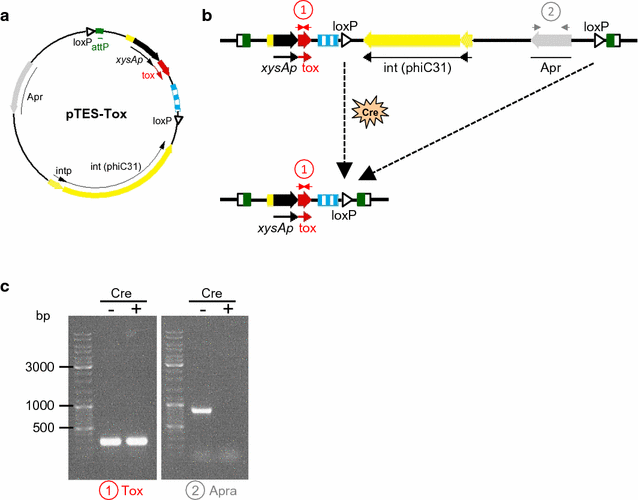
Results: In this work, a system completely free of antibiotic resistance genes and useful for the production of high yields of proteins in Streptomyces is described. This system is based on the separation of the two components of the yefM/yoeBsl (antitoxin/toxin) operon; the toxin (yoeBsl) gene, responsible for host death, is integrated into the genome and the antitoxin gene (yefMsl), which inactivates the toxin, is located in the expression plasmid. To develop this system, the toxin gene was integrated into the genome of a strain lacking the complete operon, and the antibiotic resistance gene integrated along with the toxin was eliminated by Cre recombinase to generate a final host strain free of any antibiotic resistance marker. In the same way, the antibiotic resistance gene from the final expression plasmid was removed by Dre recombinase. The usefulness of this system was analysed by checking the production of two hydrolases from different Streptomyces. Production of both proteins, with potential industrial use, was high and stable over time after strain storage and after serial subcultures. These results support the robustness and stability of the positive selection system developed.
Conclusions: The total absence of antibiotic resistance genes makes this system a powerful tool for using Streptomyces as a host to produce proteins at the industrial level. This work is the first Streptomyces antibiotic marker-free system to be described. Graphical abstract Antibiotic marker-free platform for protein expression in Streptomyces. The antitoxin gene present in the expression plasmid counteracts the effect of the toxin gene in the genome. In absence of the expression plasmid, the toxin causes cell death ensuring that only plasmid-containing cells persist.
Keywords: Antibiotic marker-free; Heterologous protein expression; Separate-component-stabilization system; Streptomyces; Toxin-antitoxin.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Stable expression plasmids for Streptomyces based on a toxin-antitoxin system.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 Apr 25;12:39. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-39. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 23617558 Free PMC article.
-
Minimized antibiotic-free plasmid vector for gene therapy utilizing a new toxin-antitoxin system.Metab Eng. 2023 Sep;79:86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2023.07.003. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Metab Eng. 2023. PMID: 37451534
-
Characterization of the Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999 Derived VapC/VapB Toxin-Antitoxin System in Escherichia coli.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 1;8(7):195. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070195. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27376329 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of toxin-antitoxin systems by proteolysis.Plasmid. 2013 Jul;70(1):33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23396045 Review.
-
Preventing toxicity in toxin-antitoxin systems: An overview of regulatory mechanisms.Biochimie. 2024 Feb;217:95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.07.013. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Biochimie. 2024. PMID: 37473832 Review.
Cited by
-
A YoeB toxin cleaves both RNA and DNA.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 11;11(1):3592. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82950-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33574407 Free PMC article.
-
A highly efficient heterologous expression platform to facilitate the production of microbial natural products in Streptomyces.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 May 14;24(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02722-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40369635 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999.Mar Drugs. 2019 Apr 4;17(4):211. doi: 10.3390/md17040211. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30987346 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomycetes: Attractive Hosts for Recombinant Protein Production.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1958. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01958. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32973711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a pyrF-based counterselectable system for targeted gene deletion in Streptomyces rimosus.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021 May 15;22(5):383-396. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000606. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021. PMID: 33973420 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

