Stimulation of IL-1β and IL-6 through NF-κB and sonic hedgehog-dependent pathways in mouse astrocytes by excretory/secretory products of fifth-stage larval Angiostrongylus cantonensis
- PMID: 28950910
- PMCID: PMC5615811
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2385-0
Stimulation of IL-1β and IL-6 through NF-κB and sonic hedgehog-dependent pathways in mouse astrocytes by excretory/secretory products of fifth-stage larval Angiostrongylus cantonensis
Abstract
Background: Angiostrongylus cantonensis is an important causative agent of eosinophilic meningitis and eosinophilic meningoencephalitis in humans. Previous studies have shown that the Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway may reduce cell apoptosis by inhibiting oxidative stress in A. cantonensis infection. In this study, we investigated the relationship between cytokine secretion and Shh pathway activation after treatment with excretory/secretory products (ESP) of fifth-stage larval A. cantonensis (L5).
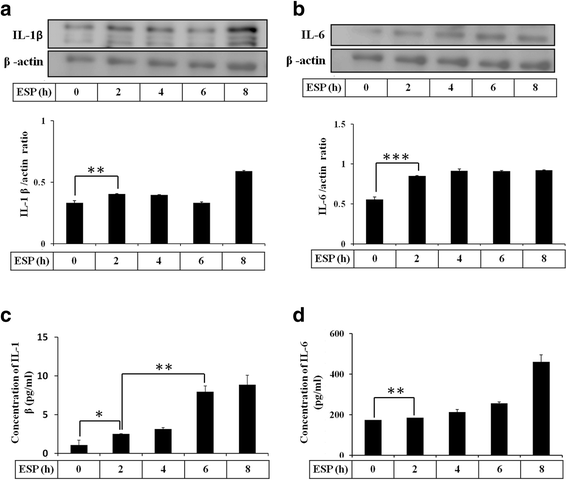
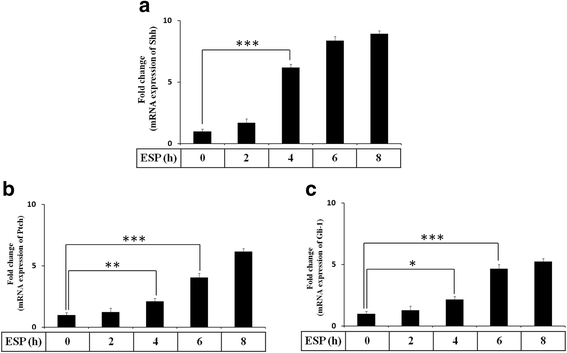
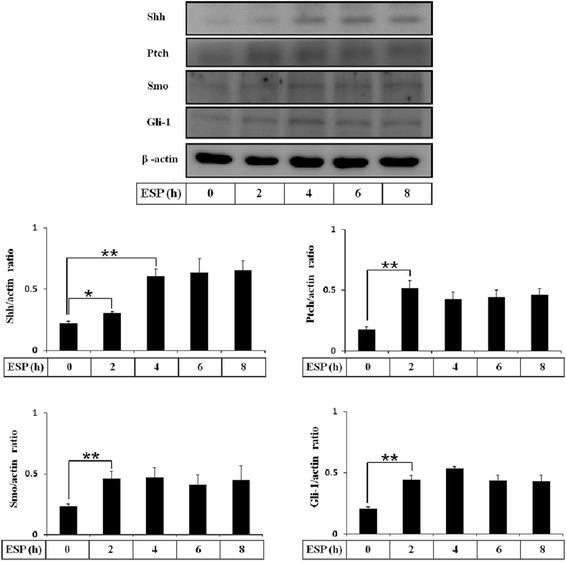
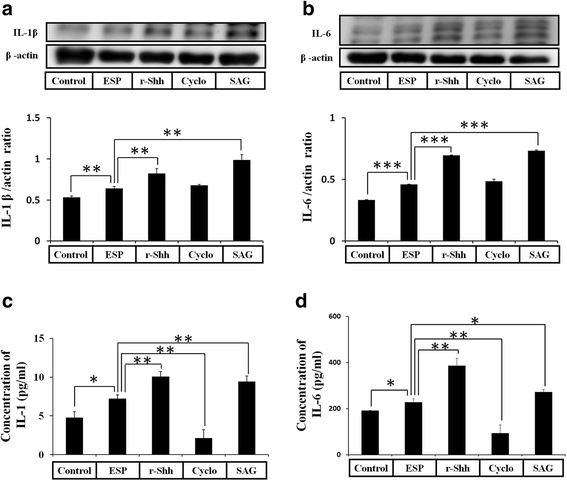
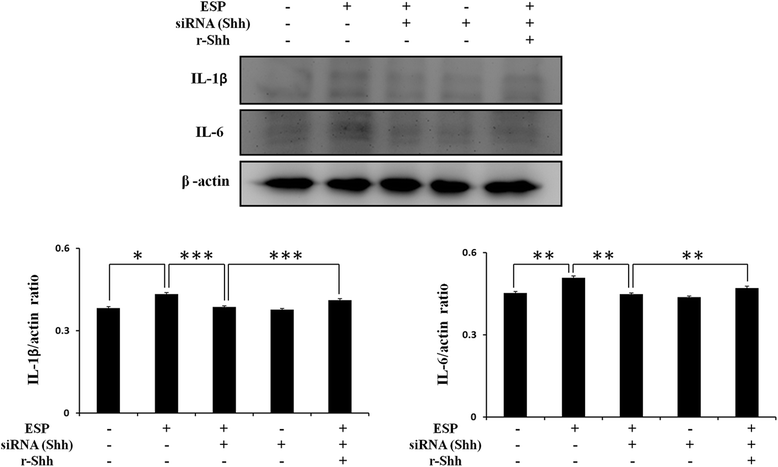
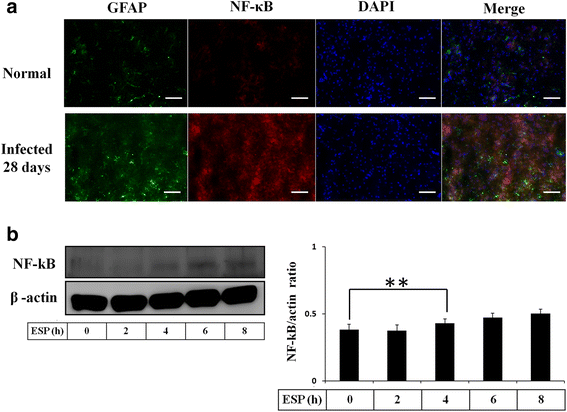
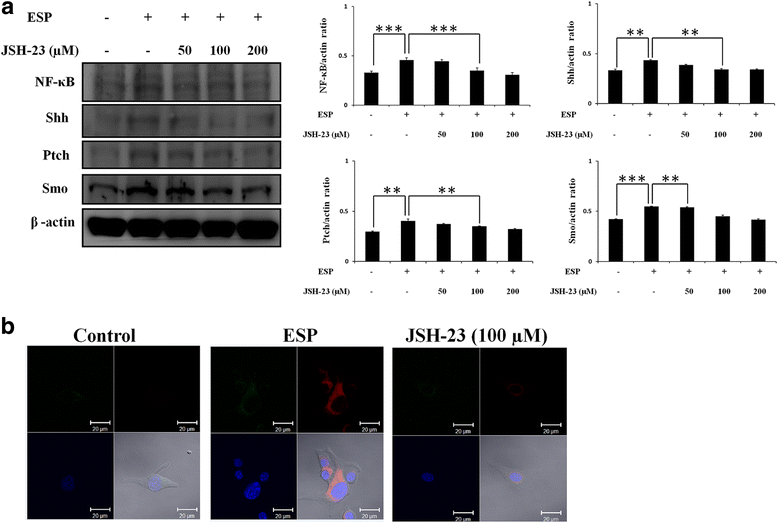
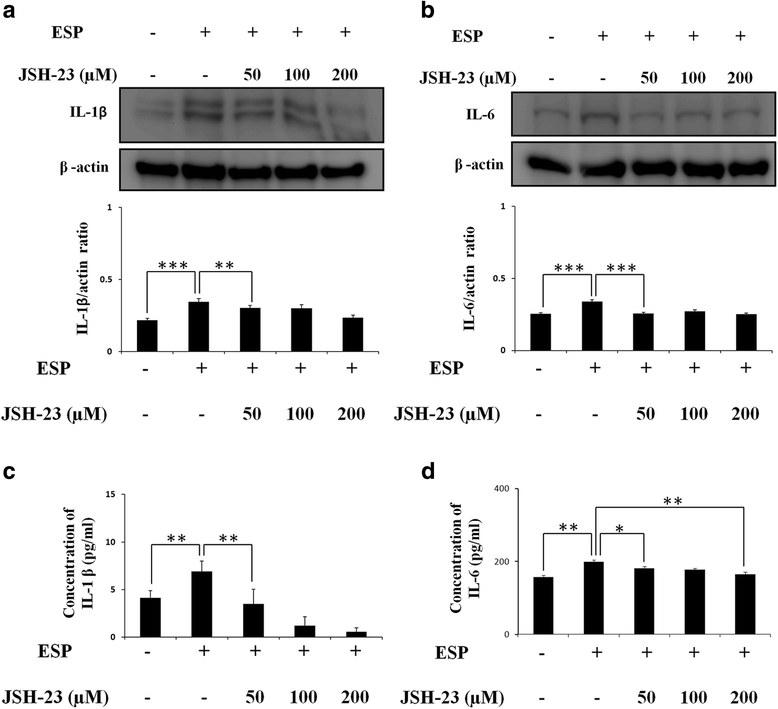
Results: The results showed that IL-1β and IL-6 levels in mouse astrocytes were increased. Moreover, ESP stimulated the protein expression of Shh pathway molecules, including Shh, Ptch, Smo and Gli-1, and induced IL-1β and IL-6 secretion. The transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) plays an important role in inflammation, and it regulates the expression of proinflammatory genes, including cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-1β and TNF-α. After ESP treatment, NF-κB induced IL-1β and IL-6 secretion in astrocytes by activating the Shh signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Overall, the data presented in this study showed that ESP of fifth-stage larval A. cantonensis stimulates astrocyte activation and cytokine generation through NF-κB and the Shh signaling pathway.
Keywords: Angiostrongylus cantonensis; Astrocytes; Cytokine; Excretory/secretory products; NF-κB; Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal protocols in this study were approved by the Chang Gung University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (CGU15–193). Mice were housed in plastic cages and provided with food and water ad libitum. The experimental animals were sacrificed by anesthesia with chloral hydrate.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

