The impact and financial burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension on patients and caregivers: results from a national survey
- PMID: 28953608
- PMCID: PMC5626251
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006783
The impact and financial burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension on patients and caregivers: results from a national survey
Abstract
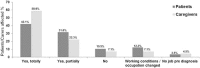
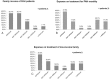
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a chronic progressive devastating disease. Symptom burden might impair health-related quality of life of patients. Furthermore, treatment on this disease brings significant financial burden to patients' families. Both physiological and psychological symptoms have been reported, but limited evidence regarding the impact of PAH on patients and caregivers exists, especially the emotional issues and their association with patients' health quality. The main purpose of this study was to describe the impact of PAH on patients and their caregivers in a Chinese population.This large-scale national survey enrolled 174 participants to complete questionnaires using face-to-face semistructured interviews.PAH influenced all aspects of patients' lives including daily activities, work, emotions, and personal relationships. Both patients and caregivers reported a major impact on family finances and on their work. The majority of patients had feelings of isolation. A lack of public understanding about PAH contributes to social isolation. Most patients and caregivers would like to get information regarding PAH doctors and patient organization contacts to obtain support.This survey-based report provides information regarding the way and extent to which PAH impacts both patients and their caregivers and provides some means for comparison with non-Chinese populations. It is important for physicians and the community to offer more support and information for PAH patients and their families.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang R, Dai LZ, Xie WP, et al. Survival of Chinese patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern treatment era. Chest 2011;140:301–9. - PubMed
-
- Rosenkranz S. Pulmonary hypertension 2015: current definitions, terminology, and novel treatment options. Clin Res Cardiol 2015;104:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Taichman DB, Mandel J. Epidemiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Chest Med 2013;34:619–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

