Massively parallel de novo protein design for targeted therapeutics
- PMID: 28953867
- PMCID: PMC5802399
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23912
Massively parallel de novo protein design for targeted therapeutics
Abstract
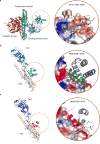
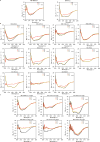
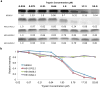
De novo protein design holds promise for creating small stable proteins with shapes customized to bind therapeutic targets. We describe a massively parallel approach for designing, manufacturing and screening mini-protein binders, integrating large-scale computational design, oligonucleotide synthesis, yeast display screening and next-generation sequencing. We designed and tested 22,660 mini-proteins of 37-43 residues that target influenza haemagglutinin and botulinum neurotoxin B, along with 6,286 control sequences to probe contributions to folding and binding, and identified 2,618 high-affinity binders. Comparison of the binding and non-binding design sets, which are two orders of magnitude larger than any previously investigated, enabled the evaluation and improvement of the computational model. Biophysical characterization of a subset of the binder designs showed that they are extremely stable and, unlike antibodies, do not lose activity after exposure to high temperatures. The designs elicit little or no immune response and provide potent prophylactic and therapeutic protection against influenza, even after extensive repeated dosing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures










References
-
- Kintzing JR, Cochran JR. Engineered knottin peptides as diagnostics, therapeutics, and drug delivery vehicles. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2016;34:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Gebauer M, Skerra A. Engineered protein scaffolds as next-generation antibody therapeutics. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009;13:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Zahnd C, et al. Efficient tumor targeting with high-affinity designed ankyrin repeat proteins: effects of affinity and molecular size. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1595–1605. - PubMed
-
- Vazquez-Lombardi R, et al. Challenges and opportunities for non-antibody scaffold drugs. Drug Discov Today. 2015;20:1271–1283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI119258/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AI119258/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1R41AI122431/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103403/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080833/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R41 AI122431/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD021527/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI127371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI117675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI123920/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091823/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI125704/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

