Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours
- PMID: 28953875
- PMCID: PMC6050590
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24028
Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours.Nature. 2018 Jun;558(7710):E1. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0111-5. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29769713
Abstract
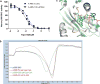
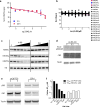
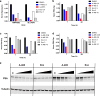
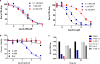
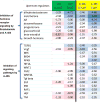
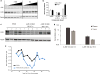
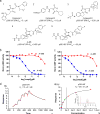
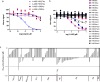
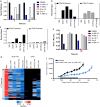
The dynamic and reversible acetylation of proteins, catalysed by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), is a major epigenetic regulatory mechanism of gene transcription and is associated with multiple diseases. Histone deacetylase inhibitors are currently approved to treat certain cancers, but progress on the development of drug-like histone actyltransferase inhibitors has lagged behind. The histone acetyltransferase paralogues p300 and CREB-binding protein (CBP) are key transcriptional co-activators that are essential for a multitude of cellular processes, and have also been implicated in human pathological conditions (including cancer). Current inhibitors of the p300 and CBP histone acetyltransferase domains, including natural products, bi-substrate analogues and the widely used small molecule C646, lack potency or selectivity. Here, we describe A-485, a potent, selective and drug-like catalytic inhibitor of p300 and CBP. We present a high resolution (1.95 Å) co-crystal structure of a small molecule bound to the catalytic active site of p300 and demonstrate that A-485 competes with acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). A-485 selectively inhibited proliferation in lineage-specific tumour types, including several haematological malignancies and androgen receptor-positive prostate cancer. A-485 inhibited the androgen receptor transcriptional program in both androgen-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer and inhibited tumour growth in a castration-resistant xenograft model. These results demonstrate the feasibility of using small molecule inhibitors to selectively target the catalytic activity of histone acetyltransferases, which may provide effective treatments for transcriptional activator-driven malignancies and diseases.
Figures


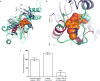
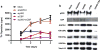
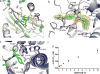
References
-
- Tessarz P, Kouzarides T. Histone core modifications regulating nucleosome structure and dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014;15:703–708. - PubMed
-
- Simon RP, Robaa D, Alhalabi Z, Sippl W, Jung M. KATching-Up on Small Molecule Modulators of Lysine Acetyltransferases. J. Med. Chem. 2016;59:1249–1270. - PubMed
-
- Iyer NG, Ozdag H, Caldas C. p300/CBP and cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:4225–4231. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanyam K, et al. Polyisoprenylated benzophenone, garcinol, a natural histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, represses chromatin transcription and alters global gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:33716–33726. - PubMed
-
- Lau OD, et al. HATs off: selective synthetic inhibitors of the histone acetyltransferases p300 and PCAF. Mol. Cell. 2000;5:589–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

