PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas
- PMID: 28953887
- PMCID: PMC5891348
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24040
PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas.Nature. 2019 Jan;565(7738):E4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0814-7. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30532003
Abstract
Targeted BRAF inhibition (BRAFi) and combined BRAF and MEK inhibition (BRAFi and MEKi) therapies have markedly improved the clinical outcomes of patients with metastatic melanoma. Unfortunately, the efficacy of these treatments is often countered by the acquisition of drug resistance. Here we investigated the molecular mechanisms that underlie acquired resistance to BRAFi and to the combined therapy. Consistent with previous studies, we show that resistance to BRAFi is mediated by ERK pathway reactivation. Resistance to the combined therapy, however, is mediated by mechanisms independent of reactivation of ERK in many resistant cell lines and clinical samples. p21-activated kinases (PAKs) become activated in cells with acquired drug resistance and have a pivotal role in mediating resistance. Our screening, using a reverse-phase protein array, revealed distinct mechanisms by which PAKs mediate resistance to BRAFi and the combined therapy. In BRAFi-resistant cells, PAKs phosphorylate CRAF and MEK to reactivate ERK. In cells that are resistant to the combined therapy, PAKs regulate JNK and β-catenin phosphorylation and mTOR pathway activation, and inhibit apoptosis, thereby bypassing ERK. Together, our results provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying acquired drug resistance to current targeted therapies, and may help to direct novel drug development efforts to overcome acquired drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
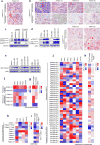



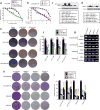
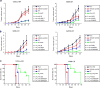





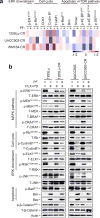
References
-
- Boussemart L, et al. eIF4F is a nexus of resistance to anti-BRAF and anti-MEK cancer therapies. Nature. 2014;513:105–109. - PubMed
-
- Larkin J, et al. Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:1867–1876. - PubMed
-
- Long GV, et al. Increased MAPK reactivation in early resistance to dabrafenib/trametinib combination therapy of BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:5694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

