Controlling Depth of Cellular Quiescence by an Rb-E2F Network Switch
- PMID: 28954237
- PMCID: PMC6571029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.09.007
Controlling Depth of Cellular Quiescence by an Rb-E2F Network Switch
Abstract
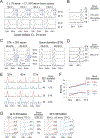
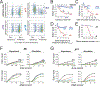
Quiescence is a non-proliferative cellular state that is critical to tissue repair and regeneration. Although often described as the G0 phase, quiescence is not a single homogeneous state. As cells remain quiescent for longer durations, they move progressively deeper and display a reduced sensitivity to growth signals. Deep quiescent cells, unlike senescent cells, can still re-enter the cell cycle under physiological conditions. Mechanisms controlling quiescence depth are poorly understood, representing a currently underappreciated layer of complexity in growth control. Here, we show that the activation threshold of a Retinoblastoma (Rb)-E2F network switch controls quiescence depth. Particularly, deeper quiescent cells feature a higher E2F-switching threshold and exhibit a delayed traverse through the restriction point (R-point). We further show that different components of the Rb-E2F network can be experimentally perturbed, following computer model predictions, to coarse- or fine-tune the E2F-switching threshold and drive cells into varying quiescence depths.
Keywords: Rb-E2F pathway; activation threshold; bistable switch; cell cycle entry; cell growth; cell proliferation; cellular quiescence; model simulation; quiescence depth; quiescence heterogeneity.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

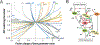
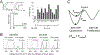

Similar articles
-
Exit from quiescence displays a memory of cell growth and division.Nat Commun. 2017 Aug 22;8(1):321. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00367-0. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28831039 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of bistability underlying mammalian cell cycle entry.Mol Syst Biol. 2011 Apr 26;7:485. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.19. Mol Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21525871 Free PMC article.
-
A bistable Rb-E2F switch underlies the restriction point.Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;10(4):476-82. doi: 10.1038/ncb1711. Epub 2008 Mar 23. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18364697
-
Modelling mammalian cellular quiescence.Interface Focus. 2014 Jun 6;4(3):20130074. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2013.0074. Interface Focus. 2014. PMID: 24904737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the retinoblastoma-E2F pathway by the ubiquitin-proteasome system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1849(10):1289-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26319102 Review.
Cited by
-
Multinucleation associated DNA damage blocks proliferation in p53-compromised cells.Commun Biol. 2021 Apr 9;4(1):451. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01979-5. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33837239 Free PMC article.
-
Quiescence Entry, Maintenance, and Exit in Adult Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 1;20(9):2158. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092158. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Cell Cycle Entry and Exit: A Single Cell Perspective.Compr Physiol. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):317-344. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190014. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31853969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Fluid Flow Induces Shallow Quiescence Through Physical and Biochemical Cues.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 24;10:792719. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.792719. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35281101 Free PMC article.
-
MAGI1 Prevents Senescence and Promotes the DNA Damage Response in ER+ Breast Cancer.Cells. 2023 Jul 25;12(15):1929. doi: 10.3390/cells12151929. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelman RC, Stein G, Roth GS, and Englander D (1972). Age-dependent regulation of mammalian DNA synthesis and cell proliferation In vivo. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 1, 49–59.
-
- Aguda BD (2015). Cell Cycle Control: The Restriction Point. eLS 1, 5.
-
- Ao P (2004). Potential in stochastic differential equations: novel construction. J Phys a-Math Gen 37, L25–L30.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

