Long-term Peripheral Neuropathy in Breast Cancer Patients Treated With Adjuvant Chemotherapy: NRG Oncology/NSABP B-30
- PMID: 28954297
- PMCID: PMC5825682
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djx162
Long-term Peripheral Neuropathy in Breast Cancer Patients Treated With Adjuvant Chemotherapy: NRG Oncology/NSABP B-30
Abstract
Background: The long-term effects of chemotherapy are sparsely reported. Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is one of the most frequent toxicities associated with taxane use for the treatment of early-stage breast cancer. We investigated the impact of the three different docetaxel-based regimens and patient characteristics on long-term, patient-reported outcomes of PN and the impact of PN on long-term quality of life (QOL).
Methods: The National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-30 was a randomized trial comparing sequential doxorubicin (A) and cyclophosphamide (C) followed by docetaxel (T) (AC→T), concurrent ACT, or AT in women with node-positive, early-stage breast cancer. The AC→T group had a higher cumulative dose of T. PN was one of the symptoms assessed in a QOL substudy. Statistical methods included simple and mixed ordinal logistic regression and general linear models. All statistical tests were two-sided.
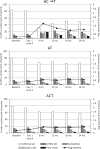
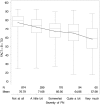
Results: Of 1512 patients, 41.9% reported PN two years after treatment initiation. Treatment with AT and ACT was associated with less severe long-term PN compared with AC→T (odds ratio [OR] = 0.45, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.35 to 0.58; OR = 0.59, 95% CI = 0.46 to 0.75). Preexisting PN, older age, obesity, mastectomy, and greater number of positive nodes were also associated with higher risk of long-term PN. Patients who reported worse PN symptoms at 24 months had statistically significantly worse QOL (Ptrend < .001).
Conclusions: The administration of docetaxel is associated with long-term PN. The lower rate of long-term PN in AT and ACT patients might be an important consideration in supporting choosing these therapies for individuals with preexisting neuropathic symptoms or other risk factors for neuropathy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00003782.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures
References
-
- Ganz PA, Dougherty PM.. Painful hands and feet after cancer treatment: Inflammation affecting the mind-body connection. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(7):649–652. - PubMed
-
- Eckhoff L, Knoop AS, Jensen MB, Ewertz M.. Persistence of docetaxel-induced neuropathy and impact on quality of life among breast cancer survivors. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51:292–300. - PubMed
-
- Hershman DL, Weimer LH, Wang A, et al. Association between patient reported outcomes and quantitative sensory tests for measuring long-term neurotoxicity in breast cancer survivors treated with adjuvant paclitaxel chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;125:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Fontes F, Pereira S, Castro-Lopes JM, Lunet N.. A prospective study on the neurological complications of breast cancer and its treatment: Updated analysis three years after cancer diagnosis. Breast. 2016;29:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Ewertz M, Qvortrup C, Eckhoff L.. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients treated with taxanes and platinum derivatives. Acta Oncologica. 2015;54:587–591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

