Durability of Protection Afforded by Fewer Doses of the HPV16/18 Vaccine: The CVT Trial
- PMID: 28954299
- PMCID: PMC6075614
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djx158
Durability of Protection Afforded by Fewer Doses of the HPV16/18 Vaccine: The CVT Trial
Abstract
Background: Previously, we demonstrated similar human papillomavirus (HPV)16/18 vaccine efficacy estimates and stable HPV16/18 antibody levels four years postvaccination in a nonrandomized analysis of women who received a varying number of doses of the bivalent HPV16/18 vaccine. Here we extend data to seven years following initial vaccination.
Methods: We evaluated HPV16/18-vaccinated women who received one (n = 134), two (n 0/1 = 193, n 0/6 = 79), or three doses (n = 2043) to a median of 6.9 years postvaccination. Cervical HPV DNA was measured with the SPF10- DEIA-LiPA PCR system; HPV16/18-specific antibody levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (n = 486). Infection and immunological measures were compared across vaccine dose groups. Prevalent HPV infection at year 7 was also compared with an unvaccinated control group (UCG). All statistical tests were two-sided.
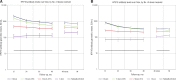
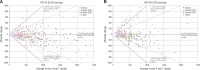
Results: Among women in the three-dose, two-dose 0/6 , two-dose 0/1 , and one-dose groups, cumulative incident HPV16/18 infection rates (No. of events/No. of individuals) were 4.3% (88/2036, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 3.5% to 5.3%), 3.8% (3/78, 95% CI = 1.0% to 10.1%), 3.6% (7/192, 95% CI = 1.6% to 7.1%), and 1.5% (2/133, 95% CI = 0.3% to 4.9%; P = 1.00, .85, .17 comparing the two-dose 0/6 , two-dose 0/1 , and one-dose groups to the three-dose group, respectively). The prevalence of other carcinogenic and noncarcinogenic HPV types, excluding HPV16/18/31/33/45, were high and not statistically different among all dose groups, indicating that the low incidence of HPV16/18 in the one- and two-dose groups was not due to lack of exposure. At seven years, 100% of participants in all dose groups remained HPV16 and HPV18 seropositive. A non-statistically significant decrease in the geometric mean of the HPV16 antibody levels between years 4 and 7 was observed among women in the three-dose group: -10.8% (95% CI = -25.3% to 6.6%); two-dose (0/6 months) group: -17.3% (95% CI = -39.3% to 12.8%), two-dose (0/1 month) group: -6.9% (95% CI = -22.1% to 11.2%), and one-dose group: -5.5% (95% CI = -29.7% to 27.0%); results were similar for HPV18.
Conclusions: At an average of seven years of follow-up, we observed similar low rates of HPV16/18 infections and slight, if any, decreases in HPV16/18 antibody levels by dose group.
Published by Oxford University Press 2017. This work is written by US Government employees and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al.Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al.Quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56(RR-2):1–24. - PubMed
-
- Bouvard V, Baan R, Straif K, et al.A review of human carcinogens—part B: Biological agents. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(4):321–322. - PubMed
-
- Bruni L, Diaz M, Barrionuevo-Rosas L, et al.Global estimates of human papillomavirus vaccination coverage by region and income level: A pooled analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2016;4(7):e453–e463. - PubMed
-
- Dobson SR, McNeil S, Dionne M, et al.Immunogenicity of 2 doses of HPV vaccine in younger adolescents vs 3 doses in young women: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;309(17):1793–1802. - PubMed

