Beneficial Effects of Small Molecule Oligopeptides Isolated from Panax ginseng Meyer on Pancreatic Beta-Cell Dysfunction and Death in Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 28954411
- PMCID: PMC5691678
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9101061
Beneficial Effects of Small Molecule Oligopeptides Isolated from Panax ginseng Meyer on Pancreatic Beta-Cell Dysfunction and Death in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
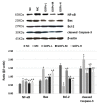
To determine whether treatment with ginseng oligopeptides (GOPs) could modulate hyperglycemia related to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in rats induced by high-fat diet and low doses of alloxan, type 2 diabetes was induced in male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats by injecting them once with 105 mg/kg alloxan and feeding them high-carbohydrate/high-fat diet with or without GOP administration (0.125, 0.5, and 2.0 g/kg Body Weight) for 7, 24, and 52 weeks. Oral glucose test tolerance (OGTT), plasma glucose, serum insulin, level of antioxidant, and beta cell function were measured. Morphological observation and immunohistochemistry study of insulin of islets was performed by light microscopy. The insulin level and the expression of NF-κB and Bcl-2 family in pancreatic islets were also detected by Western blot analysis. In addition, survival time and survival rate were observed. After the treatment, the abnormal OGTT were partially reversed by GOPs treatment in diabetic rats. The efficacy of GOPs was manifested in the amelioration of pancreatic damage, as determined by microscopy analysis. Moreover, GOPs treatment increased the normal insulin content and decreased the expression of the NF-κB-signaling pathway. Compared with those in the control model, the survival time and rate were significantly longer. It is suggested that GOPs exhibit auxiliary therapeutic potential for diabetes.
Keywords: Panax ginseng oligopeptide; alloxan; high-carbohydrate/high-fat; pancreatic beta-cell failure; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Morrison J.A., Glueck C.J., Horn P.S., Schreiber G.B., Wang P. Pre-teen insulin resistance predicts weight gain, impaired fasting glucose, and type 2 diabetes at age 18–19 years: A 10-y prospective study of black and white girls. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008;88:778–788. - PubMed
-
- Tanabe N., Saito K., Yamada Y., Takasawa T., Seki N., Suzuki H. Risk assessment by post-challenge plasma glucose, insulin response ratio, and other indices of insulin resistance and/or secretion for predicting the development of type 2 diabetes. Intern. Med. 2009;48:401–409. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.48.1325. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

