Modulation of Nrf2 by Olive Oil and Wine Polyphenols and Neuroprotection
- PMID: 28954417
- PMCID: PMC5745483
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox6040073
Modulation of Nrf2 by Olive Oil and Wine Polyphenols and Neuroprotection
Abstract
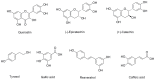
Strong adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with improved cognitive function and a lower prevalence of mild cognitive impairment. Olive oil and red wine are rich sources of polyphenols which are responsible in part for the beneficial effects on cognitive functioning. Polyphenols induce endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms by modulating transcription factors such as the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2). This review discusses the scientific data supporting the modulating effect of olive oil and red wine polyphenols on Nrf2 expression, and the potential health benefits associated with cognitive functioning.
Keywords: Nrf2; cognitive function; hydroxytyrosol; olive oil; polyphenols; resveratrol; wine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Fluid Aspect of the Mediterranean Diet in the Prevention and Management of Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes: The Role of Polyphenol Content in Moderate Consumption of Wine and Olive Oil.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 19;11(11):2833. doi: 10.3390/nu11112833. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31752333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olive oil and wine as source of multi-target agents in the prevention of Alzheimer disease.Nutr Res Rev. 2023 Jun;36(1):140-154. doi: 10.1017/S095442242100041X. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Nutr Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 34895363 Review.
-
Olive oil and red wine antioxidant polyphenols inhibit endothelial activation: antiatherogenic properties of Mediterranean diet phytochemicals.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003 Apr 1;23(4):622-9. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000062884.69432.A0. Epub 2003 Feb 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12615669
-
Mediterranean Diet, Brain and Muscle: Olive Polyphenols and Resveratrol Protection in Neurodegenerative and Neuromuscular Disorders.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(37):7595-7613. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210504113445. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33949928 Review.
-
Wine, Polyphenols, and Mediterranean Diets. What Else Is There to Say?Molecules. 2021 Sep 12;26(18):5537. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185537. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34577008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Proliferative Effects of an Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Extract Enriched in Ligstroside Aglycone and Oleocanthal on Human Liver Cancer Cell Lines.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 24;11(11):1640. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111640. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31653043 Free PMC article.
-
The Polyphenolic Composition of Extracts Derived from Different Greek Extra Virgin Olive Oils Is Correlated with Their Antioxidant Potency.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Mar 20;2019:1870965. doi: 10.1155/2019/1870965. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31015888 Free PMC article.
-
Condensed Tannins as Antioxidants in Ruminants-Effectiveness and Action Mechanisms to Improve Animal Antioxidant Status and Oxidative Stability of Products.Animals (Basel). 2021 Nov 13;11(11):3243. doi: 10.3390/ani11113243. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and Inflammatory Gene Expression Profiles of Bovine Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Response to Arthrospira platensis before and after LPS Challenge.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 20;10(5):814. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050814. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065248 Free PMC article.
-
N-of-1 Clinical Trials in Nutritional Interventions Directed at Improving Cognitive Function.Front Nutr. 2019 Jul 23;6:110. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00110. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31396517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valls-Pedret C., Lamuela-Raventós R.M., Medina-Remón A., Quintana M., Corella D., Pintó X., Martínez-González M.Á., Estruch R., Ros E. Polyphenol-rich foods in the Mediterranean diet are associated with better cognitive function in elderly subjects at high cardiovascular risk. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012;29:773–782. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources