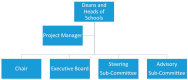
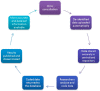
VetCompass Australia: A National Big Data Collection System for Veterinary Science
- PMID: 28954419
- PMCID: PMC5664033
- DOI: 10.3390/ani7100074
VetCompass Australia: A National Big Data Collection System for Veterinary Science
Abstract
VetCompass Australia is veterinary medical records-based research coordinated with the global VetCompass endeavor to maximize its quality and effectiveness for Australian companion animals (cats, dogs, and horses). Bringing together all seven Australian veterinary schools, it is the first nationwide surveillance system collating clinical records on companion-animal diseases and treatments. VetCompass data service collects and aggregates real-time, clinical records for researchers to interrogate, delivering sustainable and cost-effective access to data from hundreds of veterinary practitioners nationwide. Analysis of these clinical records will reveal geographical and temporal trends in the prevalence of inherited and acquired diseases, identify frequently prescribed treatments, revolutionize clinical auditing, help the veterinary profession to rank research priorities, and assure evidence-based companion-animal curricula in veterinary schools. VetCompass Australia will progress in three phases: (1) roll-out of the VetCompass platform to harvest Australian veterinary clinical record data; (2) development and enrichment of the coding (data-presentation) platform; and (3) creation of a world-first, real-time surveillance interface with natural language processing (NLP) technology. The first of these three phases is described in the current article. Advances in the collection and sharing of records from numerous practices will enable veterinary professionals to deliver a vastly improved level of care for companion animals that will improve their quality of life.
Keywords: big data; canine; companion animals; disease surveillance; electronic patient record; epidemiology; equine; feline; veterinary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Animal Medicines Australia . Pet Ownership in Australia 2016 Report. Animal Medicines Australia Pty Ltd.; Barton, Australia: 2016.
-
- Australian Companion Animal Council . Contribution of the Pet Care Industry to the Australian Economy. 7th ed. Rockwell Communications Inc.; East Kew, Victoria, Australia: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous