Newcastle Disease Virus Vectored Bivalent Vaccine against Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease and Newcastle Disease of Chickens
- PMID: 28954433
- PMCID: PMC5748598
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines5040031
Newcastle Disease Virus Vectored Bivalent Vaccine against Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease and Newcastle Disease of Chickens
Abstract
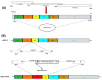
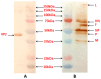
Newcastle disease virus (NDV) strain F is a lentogenic vaccine strain used for primary vaccination in day-old chickens against Newcastle disease (ND) in India and Southeast Asian countries. Recombinant NDV-F virus and another recombinant NDV harboring the major capsid protein VP2 gene of a very virulent infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV); namely rNDV-F and rNDV-F/VP2, respectively, were generated using the NDV F strain. The rNDV-F/VP2 virus was slightly attenuated, as compared to the rNDV-F virus, as evidenced from the mean death time and intracerebral pathogenicity index analysis. This result indicates that rNDV-F/VP2 behaves as a lentogenic virus and it is stable even after 10 serial passages in embryonated chicken eggs. When chickens were vaccinated with the rNDV F/VP2, it induced both humoral and cell mediated immunity, and was able to confer complete protection against very virulent IBDV challenge and 80% protection against virulent NDV challenge. These results suggest that rNDV-F could be an effective and inherently safe vaccine vector. Here, we demonstrate that a bivalent NDV-IBDV vaccine candidate generated by reverse genetics method is safe, efficacious and cost-effective, which will greatly aid the poultry industry in developing countries.
Keywords: IBDV-VP2 protein; Newcastle disease virus vector; bivalent vaccine candidate; humoral and cell mediated immune responses; protection efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Delmas B., Mundt E., Vakharia V.N., Wu J.L. Family Birnaviridae. In: Adams M.J., Carstens E.B., Lefkowitz E.J., editors. King AMQ. Academic Press; London, UK: 2012. pp. 499–507. Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

