HLAProfiler utilizes k-mer profiles to improve HLA calling accuracy for rare and common alleles in RNA-seq data
- PMID: 28954626
- PMCID: PMC5618726
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-017-0473-6
HLAProfiler utilizes k-mer profiles to improve HLA calling accuracy for rare and common alleles in RNA-seq data
Abstract
Background: The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is a genomic region involved in regulating the human immune system by encoding cell membrane major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins that are responsible for self-recognition. Understanding the variation in this region provides important insights into autoimmune disorders, disease susceptibility, oncological immunotherapy, regenerative medicine, transplant rejection, and toxicogenomics. Traditional approaches to HLA typing are low throughput, target only a few genes, are labor intensive and costly, or require specialized protocols. RNA sequencing promises a relatively inexpensive, high-throughput solution for HLA calling across all genes, with the bonus of complete transcriptome information and widespread availability of historical data. Existing tools have been limited in their ability to accurately and comprehensively call HLA genes from RNA-seq data.
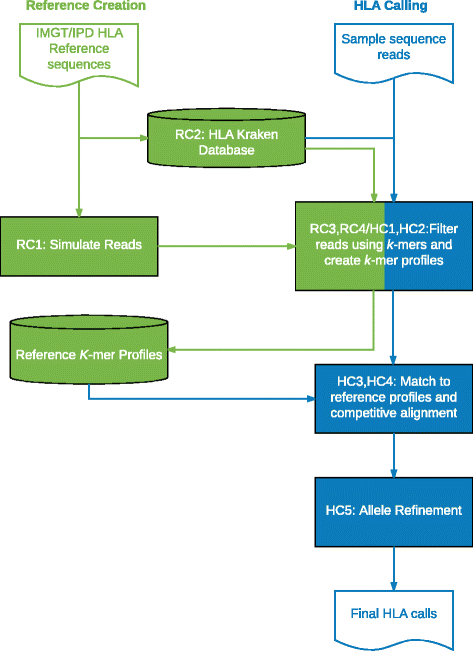
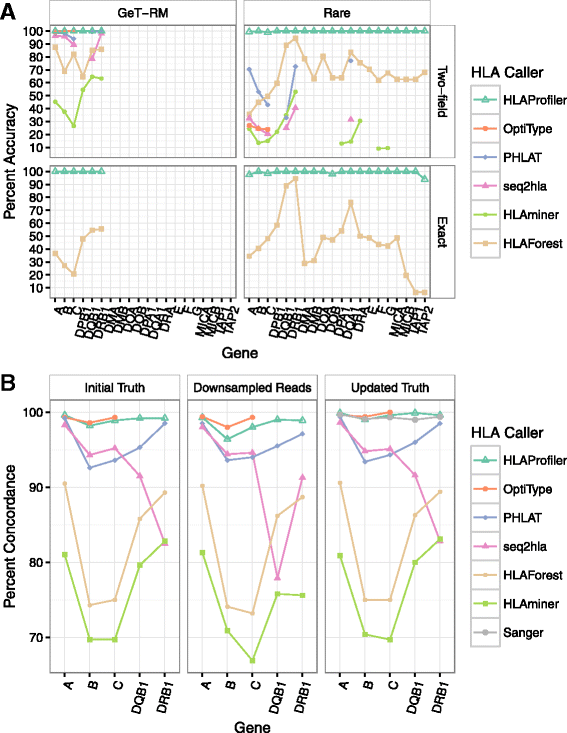
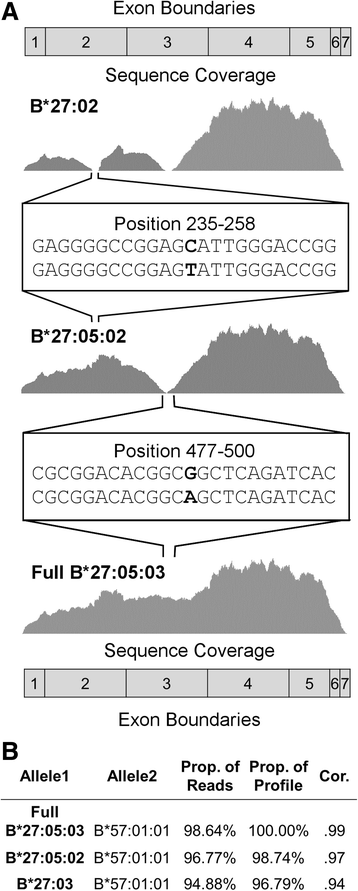
Results: We created HLAProfiler ( https://github.com/ExpressionAnalysis/HLAProfiler ), a k-mer profile-based method for HLA calling in RNA-seq data which can identify rare and common HLA alleles with > 99% accuracy at two-field precision in both biological and simulated data. For 68% of novel alleles not present in the reference database, HLAProfiler can correctly identify the two-field precision or exact coding sequence, a significant advance over existing algorithms.
Conclusions: HLAProfiler allows for accurate HLA calls in RNA-seq data, reliably expanding the utility of these data in HLA-related research and enabling advances across a broad range of disciplines. Additionally, by using the observed data to identify potential novel alleles and update partial alleles, HLAProfiler will facilitate further improvements to the existing database of reference HLA alleles. HLAProfiler is available at https://expressionanalysis.github.io/HLAProfiler/ .
Keywords: HLA; HSCT; Immunology; RNA-sequencing; Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
CCB is currently Senior Scientisit, OmicSoft Corporation, Cary, NC, 27513, USA.
KR is currently Senior Translational Scientist at Renaissance Computing Institute (RENCI), University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
MLB, CCB, KR, SW, and JGP contributed to this manuscript as employees of Q2 Solutions|EA Genomics, which offers genomic services to a variety of clients, including pharmaceutical companies. The submitted work was performed independently of these client relationships. CCB is currently an employee of OmicSoft Corporation, and this work was completed independently of that role. ETW reports personal fees and non-financial support from Illumina, outside the submitted work. BGV and SC declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Coico R, Sunshine G. Immunology: a short course. Canada: Wiley; 2015.
-
- Owen J, Punt J, Kuby J, Stranford S. Kuby Immunology. New York: Freeman; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

